LINC02418 promotes colon cancer progression by suppressing apoptosis via interaction with miR-34b-5p/BCL2 axis
- PMID: 32973404
- PMCID: PMC7507712
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-020-01530-2
LINC02418 promotes colon cancer progression by suppressing apoptosis via interaction with miR-34b-5p/BCL2 axis
Abstract
Background: LncRNAs act as functional regulators in tumor progression through interacting with various signaling pathways in multiple types of cancer. However, the effect of LINC02418 on colorectal cancer (CRC) progression and the underling mechanisms remain unclear.
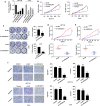
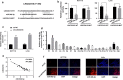
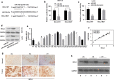
Methods: LncRNA expression profile in CRC tissues was investigated by the TCGA database. The expressional level of LINC02418 in CRC patients was determined by quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). Kaplan-Meier analyses was used to investigate the correlation between LINC02418 and overall survival (OS) of CRC patients. Cell proliferative, migratory and invasive abilities were detected by CCK-8 assays, colony formation assays and trans-well assays in HCT116 and LoVo cells which were stably transduced with sh-LINC02418 or sh-NC. The binding between LINC02418 and miR-34b-5p, and the interaction between miR-34b-5p and BCL2 were determined by dual-luciferase assays. Western blot experiments were conducted to further explore the effect of miR-34b-5p on BCL2 signaling pathway. Rescue experiments were performed to uncover the role of LINC02418/miR-34b-5p/BCL2 axis in CRC progression.
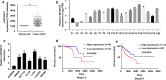
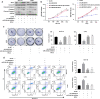
Results: LINC02418 was upregulated in human colon cancer samples when compared with adjacent tissue, and its high expressional level correlated with poor prognosis of CRC patients. LINC02418 promoted cancer progression by enhancing tumor growth, cell mobility and invasiveness of colon cancer cells. Additionally, LINC02418 could physically bind to miR-34b-5p and subsequently affect BCL2 signaling pathway. Down-regulation of LINC02418 reduced cell proliferation, while transfection of miR-34b-5p inhibitor or BCL2 into LINC02418-silenced CRC cells significantly promoted CRC cells growth.
Conclusions: LINC02418 was upregulated in human CRC samples and could be used as the indicator for prediction of prognosis. LINC02418 acted as a tumor driver by negatively regulating cell apoptosis through LINC02418/miR-34b-5p/BCL2 axis in CRC.
Keywords: BCL2; Colorectal cancer; LINC02418; ceRNA; microRNA-34b-5p.
© The Author(s) 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Feb: World cancer report 2014. World Health Organization 2015.
-
- Kanth P, Grimmett J, Champine M, Burt R, Samadder NJ. Hereditary colorectal polyposis and cancer syndromes: a primer on diagnosis and management. Am J Gastroenterol. 2017;112(10):1509–1525. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

