MicroRNAs in Alzheimer's Disease: Function and Potential Applications as Diagnostic Biomarkers
- PMID: 32973449
- PMCID: PMC7471745
- DOI: 10.3389/fnmol.2020.00160
MicroRNAs in Alzheimer's Disease: Function and Potential Applications as Diagnostic Biomarkers
Abstract
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the most common form of dementia. Although the incidence of AD is high, the rates of diagnosis and treatment are relatively low. Moreover, effective means for the diagnosis and treatment of AD are still lacking. MicroRNAs (miRNAs, miRs) are non-coding RNAs that play regulatory roles by targeting mRNAs. The expression of miRNAs is conserved, temporal, and tissue-specific. Impairment of microRNA function is closely related to AD pathogenesis, including the beta-amyloid and tau hallmarks of AD, and there is evidence that the expression of some microRNAs differs significantly between healthy people and AD patients. These properties of miRNAs endow them with potential diagnostic and therapeutic value in the treatment of this debilitating disease. This review provides comprehensive information about the regulatory function of miRNAs in AD, as well as potential applications as diagnostic biomarkers.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; biomarker; diagnosis; microRNAs; pathogenesis.
Copyright © 2020 Wei, Wang, Ma, Zhang, Cao and Li.
Figures
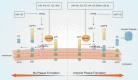
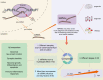
References
-
- Arena A., Iyer A. M., Milenkovic I., Kovacs G. G., Ferrer I., Perluigi M., et al. (2017). Developmental expression and dysregulation of miR-146a and miR-155 in down’s syndrome and mouse models of down’s syndrome and Alzheimer’s disease. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 14 1305–1317. 10.2174/1567205014666170706112701 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

