The CNS Myelin Proteome: Deep Profile and Persistence After Post-mortem Delay
- PMID: 32973451
- PMCID: PMC7466725
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2020.00239
The CNS Myelin Proteome: Deep Profile and Persistence After Post-mortem Delay
Abstract
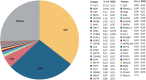
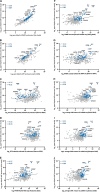
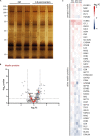
Myelin membranes are dominated by lipids while the complexity of their protein composition has long been considered to be low. However, numerous additional myelin proteins have been identified since. Here we revisit the proteome of myelin biochemically purified from the brains of healthy c56Bl/6N-mice utilizing complementary proteomic approaches for deep qualitative and quantitative coverage. By gel-free, label-free mass spectrometry, the most abundant myelin proteins PLP, MBP, CNP, and MOG constitute 38, 30, 5, and 1% of the total myelin protein, respectively. The relative abundance of myelin proteins displays a dynamic range of over four orders of magnitude, implying that PLP and MBP have overshadowed less abundant myelin constituents in initial gel-based approaches. By comparisons with published datasets we evaluate to which degree the CNS myelin proteome correlates with the mRNA and protein abundance profiles of myelin and oligodendrocytes. Notably, the myelin proteome displays only minor changes if assessed after a post-mortem delay of 6 h. These data provide the most comprehensive proteome resource of CNS myelin so far and a basis for addressing proteomic heterogeneity of myelin in mouse models and human patients with white matter disorders.
Keywords: autopsy; central nervous system (CNS); demyelination; label-free proteomics; myelin proteome; oligodendrocyte; post-mortem delay; transcriptome.
Copyright © 2020 Jahn, Siems, Kusch, Hesse, Jung, Liepold, Uecker, Sun and Werner.
Figures

References
-
- Ambrozkiewicz M. C., Schwark M., Kishimoto-Suga M., Borisova E., Hori K., Salazar-Lázaro A., et al. (2018). Polarity Acquisition in Cortical Neurons Is Driven by Synergistic Action of Sox9-Regulated Wwp1 and Wwp2 E3 Ubiquitin Ligases and Intronic miR-140. Neuron 100:1097-1115.e15. 10.1016/j.neuron.2018.10.008 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

