The Melanocortin System in Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar L.) and Its Role in Appetite Control
- PMID: 32973463
- PMCID: PMC7471746
- DOI: 10.3389/fnana.2020.00048
The Melanocortin System in Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar L.) and Its Role in Appetite Control
Abstract
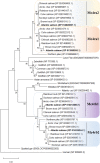
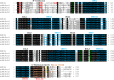
The melanocortin system is a key neuroendocrine network involved in the control of food intake and energy homeostasis in vertebrates. Within the hypothalamus, the system comprises two main distinct neuronal cell populations that express the neuropeptides proopiomelanocortin (POMC; anorexigenic) or agouti-related protein (AGRP; orexigenic). Both bind to the melanocortin-4 receptor (MC4R) in higher order neurons that control both food intake and energy expenditure. This system is relatively well-conserved among vertebrates. However, in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.), the salmonid-specific fourth round whole-genome duplication led to the presence of several paralog genes which might result in divergent functions of the duplicated genes. In the current study, we report the first comprehensive comparative identification and characterization of Mc4r and extend the knowledge of Pomc and Agrp in appetite control in Atlantic salmon. In silico analysis revealed multiple paralogs for mc4r (a1, a2, b1, and b2) in the Atlantic salmon genome and confirmed the paralogs previously described for pomc (a1, a2, and b) and agrp (1 and 2). All Mc4r paralogs are relatively well-conserved with the human homolog, sharing at least 63% amino acid sequence identity. We analyzed the mRNA expression of mc4r, pomc, and agrp genes in eight brain regions of Atlantic salmon post-smolt under two feeding states: normally fed and fasted for 4 days. The mc4ra2 and b1 mRNAs were predominantly and equally abundant in the hypothalamus and telencephalon, the mc4rb2 in the hypothalamus, and a1 in the telencephalon. All pomc genes were highly expressed in the pituitary, followed by the hypothalamus and saccus vasculosus. The agrp genes showed a completely different expression pattern from each other, with prevalent expression of the agrp1 in the hypothalamus and agrp2 in the telencephalon. Fasting did not induce any significant changes in the mRNA level of mc4r, agrp, or pomc paralogs in the hypothalamus or in other highly expressed regions between fed and fasted states. The identification and wide distribution of multiple paralogs of mc4r, pomc, and agrp in Atlantic salmon brain provide new insights and give rise to new questions of the melanocortin system in the appetite regulation in Atlantic salmon.
Keywords: Atlantic salmon; agouti-related protein (agrp); appetite control centers; brain; food intake; melanocortin system; melanocortin-4 receptor (mc4r); proopiomelanocortin (pomc).
Copyright © 2020 Kalananthan, Lai, Gomes, Murashita, Handeland and Rønnestad.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Mapping key neuropeptides involved in the melanocortin system in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) brain.J Comp Neurol. 2023 Jan;531(1):89-115. doi: 10.1002/cne.25415. Epub 2022 Oct 10. J Comp Neurol. 2023. PMID: 36217593 Free PMC article.
-
Hypothalamic agrp and pomc mRNA Responses to Gastrointestinal Fullness and Fasting in Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar, L.).Front Physiol. 2020 Feb 11;11:61. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00061. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32116771 Free PMC article.
-
Regional Expression of npy mRNA Paralogs in the Brain of Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar, L.) and Response to Fasting.Front Physiol. 2021 Aug 26;12:720639. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.720639. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34512390 Free PMC article.
-
[Regulation of appetite by melanocortin and its receptors].Nihon Rinsho. 2001 Mar;59(3):431-6. Nihon Rinsho. 2001. PMID: 11268589 Review. Japanese.
-
Regulation of Agouti-Related Protein and Pro-Opiomelanocortin Gene Expression in the Avian Arcuate Nucleus.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2017 Apr 13;8:75. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2017.00075. eCollection 2017. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2017. PMID: 28450851 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of Three POMCa Genotypes in Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides) and Their Differential Physiological Responses to Feed Domestication.Animals (Basel). 2024 Dec 17;14(24):3638. doi: 10.3390/ani14243638. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39765543 Free PMC article.
-
Divergent Pharmacology and Biased Signaling of the Four Melanocortin-4 Receptor Isoforms in Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss).Biomolecules. 2023 Aug 16;13(8):1248. doi: 10.3390/biom13081248. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37627313 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping key neuropeptides involved in the melanocortin system in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) brain.J Comp Neurol. 2023 Jan;531(1):89-115. doi: 10.1002/cne.25415. Epub 2022 Oct 10. J Comp Neurol. 2023. PMID: 36217593 Free PMC article.
-
Melanocortin receptor 3 and 4 mRNA expression in the adult female Syrian hamster brain.Front Mol Neurosci. 2023 Feb 23;16:1038341. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2023.1038341. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36910260 Free PMC article.
-
Neuropeptide Y and melanocortin receptors in fish: regulators of energy homeostasis.Mar Life Sci Technol. 2021 Sep 13;4(1):42-51. doi: 10.1007/s42995-021-00106-x. eCollection 2022 Feb. Mar Life Sci Technol. 2021. PMID: 37073356 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Agulleiro M. J., Cortés R., Leal E., Ríos D., Sánchez E., Cerdá-Reverter J. M. (2014). Characterization, tissue distribution and regulation by fasting of the agouti family of peptides in the sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 205 251–259. 10.1016/j.ygcen.2014.02.009 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

