The Phosphatase PP2A Interacts With ArnA and ArnB to Regulate the Oligomeric State and the Stability of the ArnA/B Complex
- PMID: 32973695
- PMCID: PMC7472852
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.01849
The Phosphatase PP2A Interacts With ArnA and ArnB to Regulate the Oligomeric State and the Stability of the ArnA/B Complex
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: The Phosphatase PP2A Interacts With ArnA and ArnB to Regulate the Oligomeric State and the Stability of the ArnA/B Complex.Front Microbiol. 2020 Oct 30;11:608420. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.608420. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33250888 Free PMC article.
Abstract
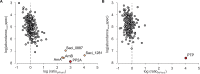
In the crenarchaeon Sulfolobus acidocaldarius, the archaellum, a type-IV pilus like motility structure, is synthesized in response to nutrient starvation. Synthesis of components of the archaellum is controlled by the archaellum regulatory network (arn). Protein phosphorylation plays an important role in this regulatory network since the deletion of several genes encoding protein kinases and the phosphatase PP2A affected cell motility. Several proteins in the archaellum regulatory network can be phosphorylated, however, details of how phosphorylation levels of different components affect archaellum synthesis are still unknown. To identify proteins interacting with the S. acidocaldarius phosphatases PTP and PP2A, co-immunoprecipitation assays coupled to mass spectrometry analysis were performed. Thirty minutes after growth in nutrient starvation medium, especially a conserved putative ATP/GTP binding protein (Saci_1281), a universal stress protein (Saci_0887) and the archaellum regulators ArnA and ArnB were identified as highly abundant interaction proteins of PP2A. The interaction between ArnA, ArnB, and PP2A was further studied. Previous studies showed that the Forkhead-associated domain containing ArnA interacts with von Willebrand type A domain containing ArnB, and that both proteins could be phosphorylated by the kinase ArnC in vitro. The ArnA/B heterodimer was reconstituted from the purified proteins. In complex with ArnA, phosphorylation of ArnB by the ArnC kinase was strongly stimulated and resulted in formation of (ArnA/B)2 and higher oligomeric complexes, while association and dephosphorylation by PP2A resulted in dissociation of these ArnA/B complexes.
Keywords: Crenarchaea; archaellum; archaellum regulation; protein interaction; protein phosphatases; protein phosphorylation.
Copyright © 2020 Ye, Vogt, van der Does, Bildl, Schulte, Essen and Albers.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Expanding the archaellum regulatory network - the eukaryotic protein kinases ArnC and ArnD influence motility of Sulfolobus acidocaldarius.Microbiologyopen. 2017 Feb;6(1):e00414. doi: 10.1002/mbo3.414. Epub 2016 Oct 22. Microbiologyopen. 2017. PMID: 27771939 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and interactions of the archaeal motility repression module ArnA-ArnB that modulates archaellum gene expression in Sulfolobus acidocaldarius.J Biol Chem. 2019 May 3;294(18):7460-7471. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.007709. Epub 2019 Mar 22. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30902813 Free PMC article.
-
Corrigendum: The Phosphatase PP2A Interacts With ArnA and ArnB to Regulate the Oligomeric State and the Stability of the ArnA/B Complex.Front Microbiol. 2020 Oct 30;11:608420. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.608420. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33250888 Free PMC article.
-
Phospholipase C-related but catalytically inactive protein, PRIP as a scaffolding protein for phospho-regulation.Adv Biol Regul. 2013 Sep;53(3):331-40. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2013.07.001. Epub 2013 Jul 17. Adv Biol Regul. 2013. PMID: 23911386 Review.
-
Protein phosphatase 2A: a highly regulated family of serine/threonine phosphatases implicated in cell growth and signalling.Biochem J. 2001 Feb 1;353(Pt 3):417-39. doi: 10.1042/0264-6021:3530417. Biochem J. 2001. PMID: 11171037 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Methods to Analyze Motility in Eury- and Crenarchaea.Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2522:373-385. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2445-6_25. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 36125764
-
Scattering-based Light Microscopy: From Metal Nanoparticles to Single Proteins.Chem Rev. 2021 Oct 13;121(19):11937-11970. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.1c00271. Epub 2021 Sep 29. Chem Rev. 2021. PMID: 34587448 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the structural landscape of universal stress proteins in Archaea.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2025 Jun 11;41(6):196. doi: 10.1007/s11274-025-04439-y. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40498147 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A comprehensive history of motility and Archaellation in Archaea.FEMS Microbes. 2021 Apr 8;2:xtab002. doi: 10.1093/femsmc/xtab002. eCollection 2021. FEMS Microbes. 2021. PMID: 37334237 Free PMC article.
-
The FHA domain protein ArnA functions as a global DNA damage response repressor in the hyperthermophilic archaeon Saccharolobus islandicus.mBio. 2023 Aug 31;14(4):e0094223. doi: 10.1128/mbio.00942-23. Epub 2023 Jun 30. mBio. 2023. PMID: 37389462 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

