Affective Immunology: The Crosstalk Between Microglia and Astrocytes Plays Key Role?
- PMID: 32973758
- PMCID: PMC7468391
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01818
Affective Immunology: The Crosstalk Between Microglia and Astrocytes Plays Key Role?
Abstract
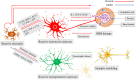
Emerging evidence demonstrates the critical role of the immune response in the mechanisms relating to mood disorders, such as major depression (MDD) and bipolar disorder (BD). This has cast a spotlight on a specialized branch committed to the research of dynamics of the fine interaction between emotion (or affection) and immune response, which has been termed as "affective immunology." Inflammatory cytokines and gut microbiota are actively involved in affective immunology. Furthermore, abnormalities of the astrocytes and microglia have been observed in mood disorders from both postmortem and molecular imaging studies; however, the underlying mechanisms remain elusive. Notably, the crosstalk between astrocyte and microglia acts as a mutual and pivotal intermediary factor modulating the immune response posed by inflammatory cytokines and gut microbiota. In this study, we propose the "altered astrocyte-microglia crosstalk (AAMC)" hypothesis which suggests that the astrocyte-microglia crosstalk regulates emotional alteration through mediating immune response, and thus, contributing to the development of mood disorders.
Keywords: astrocyte-microglia crosstalk; bipolar disorder; depression; mood disorders; neuroinflammation.
Copyright © 2020 Yang, Zhou, Jia, Qi, Tu and Shao.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Postmortem evidence of brain inflammatory markers in bipolar disorder: a systematic review.Mol Psychiatry. 2020 Jan;25(1):94-113. doi: 10.1038/s41380-019-0448-7. Epub 2019 Jun 27. Mol Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 31249382
-
Microglia-Astrocyte Crosstalk: An Intimate Molecular Conversation.Neuroscientist. 2019 Jun;25(3):227-240. doi: 10.1177/1073858418783959. Epub 2018 Jun 22. Neuroscientist. 2019. PMID: 29931997 Review.
-
Dysregulation of the gut-brain-skin axis and key overlapping inflammatory and immune mechanisms of psoriasis and depression.Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 May;137:111065. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.111065. Epub 2021 Feb 1. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 33540138 Review.
-
Glial neuroimmune signaling in opioid reward.Brain Res Bull. 2020 Feb;155:102-111. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2019.11.012. Epub 2019 Nov 29. Brain Res Bull. 2020. PMID: 31790721 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring neuroglial signaling: diversity of molecules implicated in microglia-to-astrocyte neuroimmune communication.Rev Neurosci. 2024 Sep 3;36(1):91-117. doi: 10.1515/revneuro-2024-0081. Print 2025 Jan 29. Rev Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39240134 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cognitive Functions, Neurotransmitter Alterations, and Hippocampal Microstructural Changes in Mice Caused by Feeding on Western Diet.Cells. 2023 Sep 21;12(18):2331. doi: 10.3390/cells12182331. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37759553 Free PMC article.
-
Repetitive binge-like consumption based on the Drinking-in-the-Dark model alters the microglial population in the mouse hippocampus.J Integr Neurosci. 2021 Dec 30;20(4):933-943. doi: 10.31083/j.jin2004094. J Integr Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34997716 Free PMC article.
-
The role of immune cells and associated immunological factors in the immune response to spinal cord injury.Front Immunol. 2023 Jan 5;13:1070540. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1070540. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36685599 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glioma-associated microglia/macrophages (GAMs) in glioblastoma: Immune function in the tumor microenvironment and implications for immunotherapy.Front Immunol. 2023 Mar 9;14:1123853. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1123853. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36969167 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Astrocyte-Microglia Crosstalk: A Novel Target for the Treatment of Migraine.Aging Dis. 2024 May 7;15(3):1277-1288. doi: 10.14336/AD.2023.0623. Aging Dis. 2024. PMID: 37450927 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

