T Helper (Th) Cell Profiles in Pregnancy and Recurrent Pregnancy Losses: Th1/Th2/Th9/Th17/Th22/Tfh Cells
- PMID: 32973809
- PMCID: PMC7461801
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.02025
T Helper (Th) Cell Profiles in Pregnancy and Recurrent Pregnancy Losses: Th1/Th2/Th9/Th17/Th22/Tfh Cells
Abstract
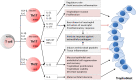
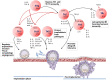
During pregnancy, various immune effectors and molecules participating in the immune-microenvironment establish specific maternal tolerance toward the semi-allogeneic fetus. Activated maternal immune effectors by the trophoblast antigens, such as T helper (Th), T cytotoxic (Tc), T regulatory (Treg), and B cells, are involved in the regulation of adaptive immunity. Recognition of active signal through the T cell receptors stimulate the differentiation of naive CD3+CD4+ T cells into specific T cell subsets, such as Th1, Th2, Th9, Th17, Th22, and follicular Th cells (Tfh). Each of these subsets has a significant and distinct role in human pregnancy. Th1 immunity, characterized by immune-inflammatory responses, becomes dominant during the peri-implantation period, and the "controlled" Th1 immunity benefits the invading trophoblasts rather than harm. Quickly after the placental implantation, the early inflammatory Th1 immunity is shifted to the Th2 anti-inflammatory immune responses. The predominant Th2 immunity, which overrules the Th1 immunity at the placental implantation site, protects a fetus by balancing Th1 immunity and accommodate fetal and placental development. Moreover, Treg and Th9 cells regulate local inflammatory immune responses, potentially detrimental to the fetus. Th17 cells induce protective immunity against extracellular microbes during pregnancy. However, excessive Th17 immunity may induce uncontrolled neutrophil infiltration at the maternal-fetal interface. Other Th cell subsets such as Tfh cells, also contribute to pregnancy by setting up favorable humoral immunity during pregnancy. However, dysregulation of Th cell immunity during pregnancy may result in obstetrical complications, such as recurrent pregnancy losses (RPL) and preeclampsia (PE). With this review, we intend to deliver a comprehensive overview of CD4+ Th cell subsets, including Th1, Th2, Th9, Th17, Th22, and Tfh cells, in human pregnancy by reviewing their roles in normal and pathological pregnancies.
Keywords: Th1 cell; Th17 cells; Th2 cells; Th22 cells; Th9 cells; pregnancy; recurrent pregnancy loss.
Copyright © 2020 Wang, Sung, Gilman-Sachs and Kwak-Kim.
Figures
References
-
- Mosmann TR, Cherwinski H, Bond MW, Giedlin MA, Coffman RL. Two types of murine helper T cell clone. I. Definition according to profiles of lymphokine activities and secreted proteins. J Immunol. (1986) 136:2348–57. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

