Influence of Genetic Variance on Biomarker Levels After Occupational Exposure to 1,6-Hexamethylene Diisocyanate Monomer and 1,6-Hexamethylene Diisocyanate Isocyanurate
- PMID: 32973864
- PMCID: PMC7466756
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2020.00836
Influence of Genetic Variance on Biomarker Levels After Occupational Exposure to 1,6-Hexamethylene Diisocyanate Monomer and 1,6-Hexamethylene Diisocyanate Isocyanurate
Abstract
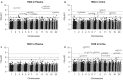
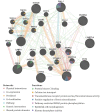
We evaluated the impact of genetic variance on biomarker levels in a population of workers in the automotive repair and refinishing industry who were exposed to respiratory sensitizers 1,6-hexamethylene diisocyanate (HDI) monomer and one of its trimers, HDI isocyanurate. The exposures and respective urine and plasma biomarkers 1,6-diaminohexane (HDA) and trisaminohexyl isocyanurate (TAHI) were measured in 33 workers; and genome-wide microarrays (Affymetrix 6.0) were used to genotype the workers' single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). Linear mixed model analyses have indicated that interindividual variations in both inhalation and skin exposures influenced these biomarker levels. Using exposure values as covariates and a false discovery rate < 0.10 to assess statistical significance, we observed that seven SNPs were associated with HDA in plasma, five were associated with HDA in urine, none reached significance for TAHI in plasma, and eight were associated with TAHI levels in urine. The different genotypes for the 20 significant SNPs accounted for 4- to 16-fold changes observed in biomarker levels. Associated gene functions include transcription regulation, calcium ion transport, vascular morphogenesis, and transforming growth factor beta signaling pathway, which may impact toxicokinetics indirectly by altering inflammation levels. Additionally, in an expanded analysis using a minor allele cutoff of 0.05 instead of 0.10, there were biomarker-associated SNPs within three genes that have been associated with isocyanate-induced asthma: ALK, DOCK2, and LHPP. We demonstrate that genetic variance impacts the biomarker levels in workers exposed to HDI monomer and HDI isocyanurate and that genetics can be used to refine exposure predictions in small cohorts when quantitative personal exposure and biomarker measurements are included in the models.
Keywords: biomarkers; biomonitoring; exposure assessment; gene–environment interactions; genome-wide association study; isocyanates.
Copyright © 2020 Taylor, French, Robbins, Boyer and Nylander-French.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Epigenetic Markers Are Associated With Differences in Isocyanate Biomarker Levels in Exposed Spray-Painters.Front Genet. 2021 Jul 14;12:700636. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.700636. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34335698 Free PMC article.
-
Trisaminohexyl isocyanurate, a urinary biomarker of HDI isocyanurate exposure.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2018 Feb 15;1076:117-129. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2018.01.021. Epub 2018 Jan 31. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2018. PMID: 29406025 Free PMC article.
-
Exposures and urinary biomonitoring of aliphatic isocyanates in construction metal structure coating.Int J Hyg Environ Health. 2020 May;226:113495. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheh.2020.113495. Epub 2020 Feb 28. Int J Hyg Environ Health. 2020. PMID: 32120250
-
Urine 1,6-hexamethylene diamine (HDA) levels among workers exposed to 1,6-hexamethylene diisocyanate (HDI).Ann Occup Hyg. 2010 Aug;54(6):678-91. doi: 10.1093/annhyg/meq041. Epub 2010 Jun 7. Ann Occup Hyg. 2010. PMID: 20530123 Free PMC article.
-
Biomonitoring for Occupational Exposure to Diisocyanates: A Systematic Review.Ann Work Expo Health. 2020 Jul 1;64(6):569-585. doi: 10.1093/annweh/wxaa038. Ann Work Expo Health. 2020. PMID: 32313948 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Epigenetic Markers Are Associated With Differences in Isocyanate Biomarker Levels in Exposed Spray-Painters.Front Genet. 2021 Jul 14;12:700636. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.700636. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34335698 Free PMC article.
-
The genetics of occupational asthma development among workers exposed to diisocyanates: A systematic literature review with meta-analysis.Front Genet. 2022 Oct 6;13:944197. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.944197. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36276967 Free PMC article.
References
-
- ACGIH. (2010). Threshold Limit Values for Chemical Substances And Physical Agents and Biological Exposure Indices. Cincinnati, OH: ACGIH.
-
- Adams W. C. (1993). Measurement of Breathing Rate and Volume in Routinely Performed Daily Activities: Final Report. contract no. A033-205. Sacramento: California Environmental Protection Agency, Air Resources Board, Research Division.
-
- Akla N., Viallard C., Popovic N., Lora Gil C., Sapieha P., Larrivée B. (2018). BMP9 (Bone Morphogenetic Protein-9)/Alk1 (Activin-Like Kinase Receptor Type I) Signaling Prevents Hyperglycemia-Induced Vascular Permeability. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 38 1821–1836. 10.1161/atvbaha.118.310733 - DOI - PubMed
-
- American Association of Blood Banks (1996). Technical Manual of the American Association of Blood Banks, 12th Edn, ed. Vengelen-Tyler V. (Bethesda: AABB; ), 730.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

