Autoimmune thyroid disease and type 1 diabetes mellitus: same pathogenesis; new perspective?
- PMID: 32973994
- PMCID: PMC7493255
- DOI: 10.1177/2042018820958329
Autoimmune thyroid disease and type 1 diabetes mellitus: same pathogenesis; new perspective?
Abstract
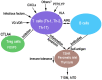
Autoimmune thyroid disease (AITD) and type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) are two common autoimmune diseases that can occur concomitantly. In general, patients with diabetes have a high risk of AITD. It has been proposed that a complex genetic basis together with multiple nongenetic factors make a variable contribution to the pathogenesis of T1DM and AITD. In this paper, we summarize current knowledge in the field regarding potential pathogenic factors of T1DM and AITD, including human leukocyte antigen, autoimmune regulator, lymphoid protein tyrosine phosphatase, forkhead box protein P3, cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen, infection, vitamin D deficiency, and chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand. These findings offer an insight into future immunotherapy for autoimmune diseases.
Keywords: autoimmune thyroid disease; autoimmunity; genetics; type 1 diabetes mellitus.
© The Author(s), 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: The author(s) declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ruggeri RM, Giuffrida G, Campenni A. Autoimmune endocrine diseases. Minerva Endocrinol 2018; 43: 305–322. - PubMed
-
- Hadj-Kacem H, Rebuffat S, Mnif-Feki M, et al. Autoimmune thyroid diseases: genetic susceptibility of thyroid-specific genes and thyroid autoantigens contributions. Int J Immunogenet 2009; 36: 85–96. - PubMed
-
- Weetman AP, McGregor AM. Autoimmune thyroid disease: further developments in our understanding. Endocr Rev 1994; 15: 788–830. - PubMed
-
- Moriguchi M, Noso S, Kawabata Y, et al. Clinical and genetic characteristics of patients with autoimmune thyroid disease with anti-islet autoimmunity. Metabolism 2011; 60: 761–766. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

