Coincidence of COVID-19 epidemic and olfactory dysfunction outbreak in Iran
- PMID: 32974228
- PMCID: PMC7500422
- DOI: 10.34171/mjiri.34.62
Coincidence of COVID-19 epidemic and olfactory dysfunction outbreak in Iran
Abstract
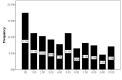
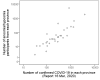
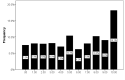
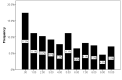
Background: The occurrence of anosmia/hyposmia during novel Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) may indicate a relationship between coincidence of olfactory dysfunction and coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). This study aimed to assess the frequency of self-reported anosmia/hyposmia during COVID-19 epidemic in Iran. Methods: This population-based cross sectional study was performed through an online questionnaire from March 12 to 17, 2020. Cases from all provinces of Iran voluntarily participated in this study. Patients completed a 33-item patient-reported online questionnaire, including smell and taste dysfunction and their comorbidities, along with their basic characteristics and past medical histories. The inclusion criteria were self-reported anosmia/hyposmia during the past 4 weeks, from the start of COVID-19 epidemic in Iran. Results: A total of 10 069 participants aged 32.5±8.6 (7-78) years took part in this study, of them 71.13% women and 81.68% nonsmokers completed the online questionnaire. The correlation between the number of olfactory disorders and reported COVID-19 patients in all provinces up to March 17, 2020 was highly significant (Spearman correlation coefficient = 0.87, P< 0.001). A sudden onset of olfactory dysfunction was reported in 76.24% of the participations and persistent anosmia in 60.90% from the start of COVID19 epidemic. In addition, 80.38% of participants reported concomitant olfactory and gustatory dysfunctions. Conclusion: An outbreak of olfactory dysfunction occurred in Iran during the COVID-19 epidemic. The exact mechanisms by which anosmia/hyposmia occurred in patients with COVID-19 call for further investigations.
Keywords: Anosmia; COVID; COVID-19; Coronavirus; Dysgeusia; ENT; Gustatory; Hyposmia; Infection; Olfaction; Olfactory; SARS-CoV-2; Smell; Taste loss.
© 2020 Iran University of Medical Sciences.
References
-
- Hummel T, Whitcroft KL, Andrews P, Altundag A, Cinghi C, Costanzo RM. et al. Position paper on olfactory dysfunction. Rhinology. 2016;56(1):1–30. - PubMed
-
- Jafek BW, Murrow B, Michaels R, Restrepo D, Linschoten M. Biopsies of human olfactory epithelium. Chem Senses. 2002;27(7):623–8. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. March 2020.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous