Polyarginine Decorated Polydopamine Nanoparticles With Antimicrobial Properties for Functionalization of Hydrogels
- PMID: 32974312
- PMCID: PMC7461895
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.00982
Polyarginine Decorated Polydopamine Nanoparticles With Antimicrobial Properties for Functionalization of Hydrogels
Abstract
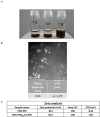
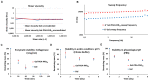
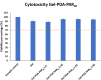
Polydopamine (PDA) nanoparticles are versatile structures that can be stabilized with proteins. In this study, we have demonstrated the feasibility of developing PDA/polypeptides complexes in the shape of nanoparticles. The polypeptide can also render the nanoparticle functional. Herein, we have developed antimicrobial nanoparticles with a narrow size distribution by decorating the polydopamine particles with a chain-length controlled antimicrobial agent Polyarginine (PAR). The obtained particles were 3.9 ± 1.7 nm in diameter and were not cytotoxic at 1:20 dilution and above. PAR-decorated nanoparticles have exhibited a strong antimicrobial activity against S. aureus, one of the most common pathogen involved in implant infections. The minimum inhibitory concentration is 5 times less than the cytotoxicity levels. Then, PAR-decorated nanoparticles have been incorporated into gelatin hydrogels used as a model of tissue engineering scaffolds. These nanoparticles have given hydrogels strong antimicrobial properties without affecting their stability and biocompatibility while improving their mechanical properties (modulus of increased storage). Decorated polydopamine nanoparticles can be a versatile tool for the functionalization of hydrogels in regenerative medicine applications by providing bioactive properties.
Keywords: antimicrobial properties; hydrogel; nanoparticles; polyarginine; polydopamine.
Copyright © 2020 Muller, Berber, Lutzweiler, Ersen, Bahri, Lavalle, Ball, Vrana and Barthes.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Injectable antimicrobial hydrogels with antimicrobial peptide and sanguinarine controlled release ability for preventing bacterial infections.Am J Transl Res. 2021 Nov 15;13(11):12614-12625. eCollection 2021. Am J Transl Res. 2021. PMID: 34956477 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering Robust Ag-Decorated Polydopamine Nano-Photothermal Platforms to Combat Bacterial Infection and Prompt Wound Healing.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022 Apr;9(11):e2106015. doi: 10.1002/advs.202106015. Epub 2022 Feb 22. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022. PMID: 35191211 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of human adipose-derived stem-cell behavior using a cell-instructive polydopamine-coated gelatin-alginate hydrogel.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2021 Dec;109(12):2597-2610. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.37253. Epub 2021 Jun 29. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2021. PMID: 34189837
-
Nanoparticles modified by polydopamine: Working as "drug" carriers.Bioact Mater. 2020 Apr 18;5(3):522-541. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2020.04.003. eCollection 2020 Sep. Bioact Mater. 2020. PMID: 32322763 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Applications of Polydopamine in Implant Surface Modification.Macromol Biosci. 2023 Oct;23(10):e2300067. doi: 10.1002/mabi.202300067. Epub 2023 Jun 3. Macromol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 37229654 Review.
Cited by
-
Fluorescent bioinspired albumin/polydopamine nanoparticles and their interactions with Escherichia coli cells.Beilstein J Nanotechnol. 2023 Dec 22;14:1208-1224. doi: 10.3762/bjnano.14.100. eCollection 2023. Beilstein J Nanotechnol. 2023. PMID: 38169939 Free PMC article.
-
Polydopamine-Based Biomaterials in Orthopedic Therapeutics: Properties, Applications, and Future Perspectives.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024 Aug 26;18:3765-3790. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S473007. eCollection 2024. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024. PMID: 39219693 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Photocatalytic and Photothermal Antimicrobial Mussel-Inspired Nanocomposites for Biomedical Applications.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 26;24(17):13272. doi: 10.3390/ijms241713272. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37686076 Free PMC article.
-
Florfenicol-Polyarginine Conjugates Exhibit Promising Antibacterial Activity Against Resistant Strains.Front Chem. 2022 Jul 1;10:921091. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2022.921091. eCollection 2022. Front Chem. 2022. PMID: 35844651 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinspired Nanoplatforms: Polydopamine and Exosomes for Targeted Antimicrobial Therapy.Polymers (Basel). 2025 Jun 16;17(12):1670. doi: 10.3390/polym17121670. Polymers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40574198 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arzillo M., Mangiapia G., Pezzella A., Heenan R. K., Radulescu A., Paduano L., et al. (2012). Eumelanin buildup on the nanoscale: aggregate growth/assembly and visible absorption development in biomimetic 5,6-dihydroxyindole polymerization. Biomacromolecules 13 2379–2390. 10.1021/bm3006159 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Butt H.-J., Graf K., Kappl M. (2013). Physics And Chemistry Of Interfaces. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

