Coagulase gene polymorphisms of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from patients at Kosti Teaching Hospital, Sudan
- PMID: 32974518
- PMCID: PMC7471778
- DOI: 10.1099/acmi.0.000026
Coagulase gene polymorphisms of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from patients at Kosti Teaching Hospital, Sudan
Abstract
Background: Staphylococcus aureus is a common cause of nosocomial infections. Epidemiological typing of S. aureus enables control of its spread. The objective of this study was to investigate coagulase gene polymorphisms of S. aureus isolated from patients at Kosti Hospital in Sudan.
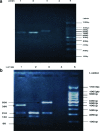
Methods: In total, 110 S. aureus isolates were recovered from 110 patients who were enrolled in the study. S. aureus strains were isolated on blood agar and MacConkey agar and then identified by conventional tests. Resistance to methicillin was determined by detection of the mecA gene. Polymorphism in the coagulase gene (coa) was investigated using PCR followed by AluI RFLP analysis.
Results: Methicillin-resistant S. aureus accounted for 62/110 (56 %) of the isolates. PCR of the coa gene showed two different amplicons, one of 680 bp detected in 83/110 (75.5 %) of the isolates and one of 790 bp detected in 27/110 (24.5 %). When digested with the AluI enzyme, the 790 bp amplicon resulted in three restriction fragments of 500, 210 and 80 bp (coa1). Restriction of the 680 bp amplicon gave two patterns; the first (coa2) was found in 22/110 (20 %) of the isolates and showed four fragments of 210, 210, 180 and 80 bp, and the second (coa3) was found in 61/110 (55.5 %) and revealed three fragments of 390, 210 and 80 bp. Most of the coa3 isolates (75.4%) were methicillin-resistant.
Conclusion: Three polymorphic genotypes of S. aureus were identified in patients at Kosti Hospital. The coa3 genotype was the predominant one and was mostly detected in methicillin-resistant isolates.
Keywords: PCR-RFLP; Staphylococcus aureus; coagulase gene polymorphism; methicillin-resistant.
© 2019 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Molecular analysis of the coagulase gene in clinical and nasal carrier isolates of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by restriction fragment length polymorphism.J Glob Antimicrob Resist. 2017 Mar;8:41-45. doi: 10.1016/j.jgar.2016.10.007. Epub 2016 Dec 9. J Glob Antimicrob Resist. 2017. PMID: 27987442
-
Analysis of methicillin-resistant and methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus by a molecular typing method based on coagulase gene polymorphisms.Epidemiol Infect. 1995 Dec;115(3):419-26. doi: 10.1017/s095026880005857x. Epidemiol Infect. 1995. PMID: 8557073 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular typing of Staphylococcus aureus based on PCR restriction fragment length polymorphism and DNA sequence analysis of the coagulase gene.J Clin Microbiol. 1998 Apr;36(4):1083-9. doi: 10.1128/JCM.36.4.1083-1089.1998. J Clin Microbiol. 1998. PMID: 9542942 Free PMC article.
-
Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism Typing of Staphylococcus aureus Strains Isolated from Bovine Mastitis and Dairy Products in Ahvaz, Iran, Using of Digested Coagulase Gene.Arch Razi Inst. 2019 Sep;74(3):303-311. doi: 10.22092/ari.2017.115900.1159. Epub 2019 Sep 1. Arch Razi Inst. 2019. PMID: 31592596
-
[Coagulase gene polymorphism in Staphylococcus aureus--a new epidemiologic marker].Immun Infekt. 1995 Feb;23(1):9-14. Immun Infekt. 1995. PMID: 7698815 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Comparative Genotypic Analysis of RAPD and RFLP Markers for Molecular Variation Detection of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Clinical Isolates.Medicina (Kaunas). 2022 Sep 8;58(9):1245. doi: 10.3390/medicina58091245. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022. PMID: 36143922 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging Challenges in Staphylococcus aureus Bloodstream Infections: Insights from Coagulase Typing, Toxin Genes, and Antibiotic Resistance Patterns.Adv Med. 2023 Dec 23;2023:7041159. doi: 10.1155/2023/7041159. eCollection 2023. Adv Med. 2023. PMID: 38162992 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Reynolds PE, Brown DF. Penicillin-binding proteins of beta-lactam-resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus. Effect of growth conditions. FEBS Lett. 1985;192:28–32. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
