Temperature-gradient incubation isolates multiple competitive species from a single environmental sample
- PMID: 32974564
- PMCID: PMC7470311
- DOI: 10.1099/acmi.0.000081
Temperature-gradient incubation isolates multiple competitive species from a single environmental sample
Abstract
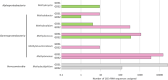
High-throughput sequencing has allowed culture-independent investigation into a wide variety of microbiomes, but sequencing studies still require axenic culture experiments to determine ecological roles, confirm functional predictions and identify useful compounds and pathways. We have developed a new method for culturing and isolating multiple microbial species with overlapping ecological niches from a single environmental sample, using temperature-gradient incubation. This method was more effective than standard serial dilution-to-extinction at isolating methanotrophic bacteria. It also highlighted discrepancies between culture-dependent and -independent techniques; 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing of the same sample did not accurately reflect cultivatable strains using this method. We propose that temperature-gradient incubation could be used to separate out and study previously 'unculturable' strains, which co-exist in both natural and artificial environments.
Keywords: 16S rRNA; Culture; Environmental sample; Isolation; Methanotroph; Temperature gradient.
© 2020 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Methanotroph diversity in landfill soil: isolation of novel type I and type II methanotrophs whose presence was suggested by culture-independent 16S ribosomal DNA analysis.Appl Environ Microbiol. 1999 Nov;65(11):4887-97. doi: 10.1128/AEM.65.11.4887-4897.1999. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1999. PMID: 10543800 Free PMC article.
-
Capturing the diversity of the human gut microbiota through culture-enriched molecular profiling.Genome Med. 2016 Jul 1;8(1):72. doi: 10.1186/s13073-016-0327-7. Genome Med. 2016. PMID: 27363992 Free PMC article.
-
Determination of the microbiological contamination in minced pork by culture dependent and 16S amplicon sequencing analysis.Int J Food Microbiol. 2019 Feb 2;290:27-35. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2018.09.025. Epub 2018 Oct 2. Int J Food Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30292676
-
Strategies for culture of 'unculturable' bacteria.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2010 Aug 1;309(1):1-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2010.02000.x. Epub 2010 Apr 27. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2010. PMID: 20487025 Review.
-
Novel approaches and reasons to isolate methanotrophic bacteria with biotechnological potentials: recent achievements and perspectives.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019 Jan;103(1):1-8. doi: 10.1007/s00253-018-9435-1. Epub 2018 Oct 12. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 30315351 Review.
Cited by
-
Thermophilic methane oxidation is widespread in Aotearoa-New Zealand geothermal fields.Front Microbiol. 2023 Aug 31;14:1253773. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1253773. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37720161 Free PMC article.
-
Expanding Characterized Diversity and the Pool of Complete Genome Sequences of Methylococcus Species, the Bacteria of High Environmental and Biotechnological Relevance.Front Microbiol. 2021 Oct 6;12:756830. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.756830. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34691008 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dopheide A, Xie D, Buckley TR, Drummond AJ, Newcomb RD. Impacts of DNA extraction and PCR on DNA metabarcoding estimates of soil biodiversity. Methods Ecol Evol. 2019;10:120–133. doi: 10.1111/2041-210X.13086. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
