Analysis of Adverse Drug Reactions with Carbamazepine and Oxcarbazepine at a Tertiary Care Hospital
- PMID: 32975062
- PMCID: PMC7515781
- DOI: 10.3349/ymj.2020.61.10.875
Analysis of Adverse Drug Reactions with Carbamazepine and Oxcarbazepine at a Tertiary Care Hospital
Abstract
Purpose: To describe adverse drug reactions (ADRs) to carbamazepine (CBZ) and oxcarbazepine (OXC), including severe cutaneous ADRs, at a tertiary care hospital over a 10-year period.
Materials and methods: The frequency and clinical features of ADRs caused by CBZ and OXC were analyzed using the pharmacovigilance database and spontaneous ADR reporting data of Yonsei University Severance Hospital & Dental Hospital (Seoul, Korea) from January 1, 2010 to January 31, 2020.
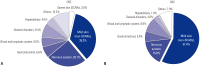
Results: Among 10419 cases prescribed CBZ and OXC, 204 ADR cases were reported. The incidences of ADRs were 1.8% and 2.2% for CBZ and OXC respectively, with no significant difference (p=0.169). The most common clinical presentations were skin disorders. Female patients had relatively more frequent ADRs than male patients. Although mild skin ADRs were more frequent with OXC, nervous system disorders, general disorders, and hepatobiliary disorders occurred more often with CBZ. There were six reports of severe cutaneous adverse reactions to CBZ, while OXC had none. Both CBZ and OXC caused ADRs at daily doses lower than the recommended initial dose.
Conclusion: Due to lower incidence of severe ADRs with OXC than CBZ, we suggest OXC as a first-line prescription.
Keywords: Carbamazepine; anticonvulsants; drug related adverse reactions; oxcarbazepine.
© Copyright: Yonsei University College of Medicine 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
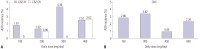
References
-
- Blom S. Trigeminal neuralgia: its treatment with a new anticonvulsant drug (G-32883) Lancet. 1962;1:839–840. - PubMed
-
- Hirschfeld RMA, Bowden CL, Gitlin MJ, Keck PE, Suppes T, Thase ME, et al. American Psychiatric Association practice guidelines for the treatment of psychiatric disorders: compendium 2002. 2nd ed. Arlington (VA): American Psychiatric Association; 2002. Practice guideline for the treatment of patients with bipolar disorder; pp. 547–634.
-
- Ghaemi SN, Berv DA, Klugman J, Rosenquist KJ, Hsu DJ. Oxcarbazepine treatment of bipolar disorder. J Clin Psychiatry. 2003;64:943–945. - PubMed
-
- Lertratanangkoon K, Horning MG. Metabolism of carbamazepine. Drug Metab Dispos. 1982;10:1–10. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

