Ferroptosis: regulated cell death
- PMID: 32975106
- PMCID: PMC7968485
- DOI: 10.2478/aiht-2020-71-3366
Ferroptosis: regulated cell death
Abstract
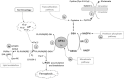
Ferroptosis is a recently identified form of regulated cell death that differs from other known forms of cell death morphologically, biochemically, and genetically. The main properties of ferroptosis are free redox-active iron and consequent iron-dependent peroxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids in cell membrane phospholipids, which results in the accumulation of lipid-based reactive oxygen species due to loss of glutathione peroxidase 4 activity. Ferroptosis has increasingly been associated with neurodegenerative diseases, carcinogenesis, stroke, intracerebral haemorrhage, traumatic brain injury, and ischemia-reperfusion injury. It has also shown a significant therapeutic potential in the treatment of cancer and other diseases. This review summarises current knowledge about and the mechanisms that regulate ferroptosis.
Feroptoza je nedavno identificirani oblik regulirane stanične smrti koji se od ostalih poznatih oblika stanične smrti razlikuje morfološki, biokemijski i genetski. Glavna svojstva feroptoze uključuju slobodno redoks aktivno željezo i posljedičnu, o željezu ovisnu, peroksidaciju polinezasićenih masnih kiselina u fosfolipidima staničnih membrana te gubitak aktivnosti glutation peroksidaze 4, što rezultira akumulacijom lipidnih, reaktivnih kisikovih spojeva. Feroptoza se sve više povezuje s raznim bolestima kao što su neurodegenerativne bolesti, karcinom, moždani udar, intracerebralna krvarenja, traumatične ozljede mozga i ishemijsko-reperfuzijska ozljeda. Također je pokazan značajan terapijski potencijal u liječenju raka i drugih bolesti. Ovaj pregled sažima trenutačne spoznaje i mehanizme koji reguliraju feroptozu.
Keywords: glutathione peroxidase 4; iron; lipid peroxidation; reactive oxygen species; system Xc−.
Figures
References
-
- Galluzzi L, Vitale I, Aaronson SA, Abrams JM, Adam D, Agostinis P, Alnemri ES, Altucci L, Amelio I, Andrews DW, Annicchiarico-Petruzzelli M, Antonov AV, Arama E, Baehrecke EH, Barlev NA, Bazan NG, Bernassola F, Bertrand MJM, Bianchi K, Blagosklonny MV, Blomgren K, Borner C, Boya P, Brenner C, Campanella M, Candi E, Carmona-Gutierrez D, Cecconi F, Chan FK, Chandel NS, Cheng EH, Chipuk JE, Cidlowski JA, Ciechanover A, Cohen GM, Conrad M, Cubillos-Ruiz JR, Czabotar PE, D’Angiolella V, Dawson TM, Dawson VL, De Laurenzi V, De Maria R, Debatin KM, DeBerardinis RJ, Deshmukh M, Di Daniele N, Di Virgilio F, Dixit VM, Dixon SJ, Duckett CS, Dynlacht BD, El-Deiry WS, Elrod JW, Fimia GM, Fulda S, García-Sáez AJ, Garg AD, Garrido C, Gavathiotis E, Golstein P, Gottlieb E, Green DR, Greene LA, Gronemeyer H, Gross A, Hajnoczky G, Hardwick JM, Harris IS, Hengartner MO, Hetz C, Ichijo H, Jäättelä M, Joseph B, Jost PJ, Juin PP, Kaiser WJ, Karin M, Kaufmann T, Kepp O, Kimchi A, Kitsis RN, Klionsky DJ, Knight RA, Kumar S, Lee SW, Lemasters JJ, Levine B, Linkermann A, Lipton SA, Lockshin RA, López-Otín C, Lowe SW, Luedde T, Lugli E, MacFarlane M, Madeo F, Malewicz M, Malorni W, Manic G, Marine JC, Martin SJ, Martinou JC, Medema JP, Mehlen P, Meier P, Melino S, Miao EA, Molkentin JD, Moll UM, Muñoz-Pinedo C, Nagata S, Nuñez G, Oberst A, Oren M, Overholtzer M, Pagano M, Panaretakis T, Pasparakis M, Penninger JM, Pereira DM, Pervaiz S, Peter ME, Piacentini M, Pinton P, Prehn JHM, Puthalakath H, Rabinovich GA, Rehm M, Rizzuto R, Rodrigues CMP, Rubinsztein DC, Rudel T, Ryan KM, Sayan E, Scorrano L, Shao F, Shi Y, Silke J, Simon HU, Sistigu A, Stockwell BR, Strasser A, Szabadkai G, Tait SWG, Tang D, Tavernarakis N, Thorburn A, Tsujimoto Y, Turk B, Vanden Berghe T, Vandenabeele P, Vander Heiden MG, Villunger A, Virgin HW, Vousden KH, Vucic D, Wagner EF, Walczak H, Wallach D, Wang Y, Wells JA, Wood W, Yuan J, Zakeri Z, Zhivotovsky B, Zitvogel L, Melino G, Kroemer G. Molecular mechanisms of cell death: recommendations of the Nomenclature Committe on Cell Death 2018. Cell Death Differ. 2018;25:486–541. doi: 10.1038/s41418-017-0012-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Galluzzi L, Bravo-San Pedro JM, Vitale I, Aaronson SA, Abrams JM, Adam D, Alnemri ES, Altucci L, Andrews D, Annicchiarico-Petruzzelli M, Baehrecke EH, Bazan NG, Bertrand MJ, Bianchi K, Blagosklonny MV, Blomgren K, Borner C, Bredesen DE, Brenner C, Campanella M, Candi E, Cecconi F, Chan FK, Chandel NS, Cheng EH, Chipuk JE, Cidlowski JA, Ciechanover A, Dawson TM, Dawson VL, De Laurenzi V, De Maria R, Debatin KM, Di Daniele N, Dixit VM, Dynlacht BD, El-Deiry WS, Fimia GM, Flavell RA, Fulda S, Garrido C, Gougeon ML, Green DR, Gronemeyer H, Hajnoczky G, Hardwick JM, Hengartner MO, Ichijo H, Joseph B, Jost PJ, Kaufmann T, Kepp O, Klionsky DJ, Knight RA, Kumar S, Lemasters JJ, Levine B, Linkermann A, Lipton SA, Lockshin RA, López-Otín C, Lugli E, Madeo F, Malorni W, Marine JC, Martin SJ, Martinou JC, Medema JP, Meier P, Melino S, Mizushima N, Moll U, Muñoz-Pinedo C, Nuñez G, Oberst A, Panaretakis T, Penninger JM, Peter ME, Piacentini M, Pinton P, Prehn JH, Puthalakath H, Rabinovich GA, Ravichandran KS, Rizzuto R, Rodrigues CM, Rubinsztein DC, Rudel T, Shi Y, Simon HU, Stockwell BR, Szabadkai G, Tait SW, Tang HL, Tavernarakis N, Tsujimoto Y, Vanden Berghe T, Vandenabeele P, Villunger A, Wagner EF, Walczak H, White E, Wood WG, Yuan J, Zakeri Z, Zhivotovsky B, Melino G, Kroemer G. Essential versus accessory aspects of cell death: recommendations of the NCCD 2015. Cell Death Differ. 2015;22:58–73. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2014.137. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

