Characteristics and Outcomes of In-Hospital Cardiac Arrest Events During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Single-Center Experience From a New York City Public Hospital
- PMID: 32975134
- PMCID: PMC7673640
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.120.007303
Characteristics and Outcomes of In-Hospital Cardiac Arrest Events During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Single-Center Experience From a New York City Public Hospital
Abstract
Background: Patients hospitalized for severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection are at risk for in-hospital cardiac arrest (IHCA). It is unknown whether certain characteristics of cardiac arrest care and outcomes of IHCAs during the COVID-19 pandemic differed compared with a pre-COVID-19 period.
Methods: All patients who experienced an IHCA at our hospital from March 1, 2020 through May 15, 2020, during the peak of the COVID-19 pandemic, and those who had an IHCA from January 1, 2019 to December 31, 2019 were identified. All patient data were extracted from our hospital's Get With The Guidelines-Resuscitation registry, a prospective hospital-based archive of IHCA data. Baseline characteristics of patients, interventions, and overall outcomes of IHCAs during the COVID-19 pandemic were compared with IHCAs in 2019, before the COVID-19 pandemic.
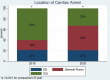
Results: There were 125 IHCAs during a 2.5-month period at our hospital during the peak of the COVID-19 pandemic compared with 117 IHCAs in all of 2019. IHCAs during the COVID-19 pandemic occurred more often on general medicine wards than in intensive care units (46% versus 33%; 19% versus 60% in 2019; P<0.001), were overall shorter in duration (median time of 11 minutes [8.5-26.5] versus 15 minutes [7.0-20.0], P=0.001), led to fewer endotracheal intubations (52% versus 85%, P<0.001), and had overall worse survival rates (3% versus 13%; P=0.007) compared with IHCAs before the COVID-19 pandemic.
Conclusions: Patients who experienced an IHCA during the COVID-19 pandemic had overall worse survival compared with those who had an IHCA before the COVID-19 pandemic. Our findings highlight important differences between these 2 time periods. Further study is needed on cardiac arrest care in patients with COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; heart arrest; hospitalization; pandemics; registries; survival rate.
Figures

References
-
- Zhou F, Yu T, Du R, Fan G, Liu Y, Liu Z, Xiang J, Wang Y, Song B, Gu X, Guan L, Wei Y, Li H, Wu X, Xu J, Tu S, Zhang Y, Chen H, Cao B. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet. 2020;395:1054–1062. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nallamothu BK, Guetterman TC, Harrod M, Kellenberg JE, Lehrich JL, Kronick SL, Krein SL, Iwashyna TJ, Saint S, Chan PS. How do resuscitation teams at top-performing hospitals for in-hospital cardiac arrest succeed? A qualitative study. Circulation. 2018;138:154–163. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.033674 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lloyd-Jones D, Adams RJ, Brown TM, Carnethon M, Dai S, De Simone G, Ferguson TB, Ford E, Furie K, Gillespie C, Go A, Greenlund K, Haase N, Hailpern S, Ho PM, Howard V, Kissela B, Kittner S, Lackland D, Lisabeth L, Marelli A, McDermott MM, Meigs J, Mozaffarian D, Mussolino M, Nichol G, Roger VL, Rosamond W, Sacco R, Sorlie P, Roger VL, Stafford R, Thom T, Wasserthiel-Smoller S, Wong ND, Wylie-Rosett J; WRITING GROUP MEMBERS; American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Heart disease and stroke statistics–2010 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2010;121:e46–e215. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.192667 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

