Association of Blood Pressure With Cause-Specific Mortality in Mexican Adults
- PMID: 32975571
- PMCID: PMC7519421
- DOI: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.18141
Association of Blood Pressure With Cause-Specific Mortality in Mexican Adults
Abstract
Importance: Elevated blood pressure is a major cause of premature death, but there is little direct evidence demonstrating this association in studies of Hispanic populations.
Objective: To assess the association between blood pressure and cause-specific mortality in a large cohort of Mexican adults with a high prevalence of uncontrolled diabetes.
Design, setting, and participants: A total of 159 755 adults aged 35 years or older from 2 districts in Mexico City were recruited to this cohort study between April 1998 and September 2004 and followed up until January 2018. The present analyses focused on 133 613 participants who were aged 35 to 74 years and had no history of chronic disease besides diabetes.
Exposure: Blood pressure.
Main outcomes and measures: Cox regression, adjusted for confounders, yielded mortality rate ratios (RRs) for deaths of participants occurring between ages 35 and 74 years.
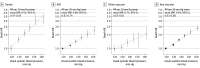
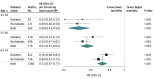
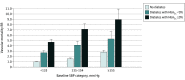
Results: Of the 133 613 participants (43 263 [32.4%] men; mean [SD] age, 50 [11] years), 16 911 (12.7%) had self-reported previously diagnosed diabetes (including 8435 [6.3%] with uncontrolled diabetes, defined as hemoglobin A1c ≥9%) and 6548 (4.9%) had undiagnosed diabetes. Systolic blood pressure (SBP) was associated with vascular mortality between ages 35 to 74 years, with each 20 mm Hg lower usual SBP associated with 35% lower vascular mortality (RR, 0.65; 95% CI, 0.61-0.68), including 48% lower stroke mortality (RR, 0.52; 95% CI, 0.47-0.59) and 32% lower ischemic heart disease mortality (RR, 0.68; 95% CI, 0.63-0.74). These RRs were broadly similar in those with and without diabetes. Compared with those without diabetes and SBP less than 135 mm Hg at recruitment, the vascular mortality RR was 2.8 (95% CI, 2.4-3.3) for those without diabetes and SBP of 155 mm Hg or greater, 4.7 (95% CI, 4.1-5.4) for those with uncontrolled diabetes and SBP less than 135 mm Hg, and 8.9 (95% CI, 7.2-11.1) for those with uncontrolled diabetes and SBP of 155 mm Hg or greater. Lower SBP was also associated with decreased kidney-related mortality (RR per 20 mm Hg lower usual SBP, 0.69; 95% CI, 0.64-0.74), decreased mortality from infection (RR, 0.81; 95% CI, 0.71-0.91), and decreased mortality from hepatobiliary disease (RR, 0.87; 95% CI, 0.78-0.98), but not decreased neoplastic or respiratory mortality. SBP was more informative for vascular mortality than other blood pressure measures (eg, compared with SBP, diastolic blood pressure was only two-thirds as informative).
Conclusions and relevance: Blood pressure was most strongly associated with vascular and kidney-related mortality in this Mexican population, with particularly high absolute excess mortality rates among individuals with diabetes. The findings reinforce the need for more widespread use of blood pressure-lowering medication in Mexico, particularly among those with diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Lewington S, Clarke R, Qizilbash N, Peto R, Collins R; Prospective Studies Collaboration . Age-specific relevance of usual blood pressure to vascular mortality: a meta-analysis of individual data for one million adults in 61 prospective studies. Lancet. 2002;360(9349):1903-1913. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(02)11911-8 - DOI - PubMed
-
- GBD 2017 Risk Factor Collaborators Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 84 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks for 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2018;392(10159):1923-1994. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32225-6 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Di Cesare M, Bentham J, Stevens GA, et al. ; NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC) . Trends in adult body-mass index in 200 countries from 1975 to 2014: a pooled analysis of 1698 population-based measurement studies with 19.2 million participants. Lancet. 2016;387(10026):1377-1396. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30054-X - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

