Association of Race and Ethnicity With Comorbidities and Survival Among Patients With COVID-19 at an Urban Medical Center in New York
- PMID: 32975574
- PMCID: PMC7519416
- DOI: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.19795
Association of Race and Ethnicity With Comorbidities and Survival Among Patients With COVID-19 at an Urban Medical Center in New York
Abstract
Importance: As of May 11, 2020, there have been more than 290 000 deaths worldwide from severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), which causes coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Risk-adjusted differences in outcomes among patients of differing ethnicity and race categories are not well characterized.
Objectives: To investigate whether presenting comorbidities in patients with COVID-19 in New York City differed by race/ethnicity and whether case fatality rates varied among different ethnic and racial groups, controlling for presenting comorbidities and other risk factors.
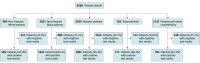
Design, setting, and participants: This cohort study included 5902 patients who presented for care to the Montefiore Medical Center, a large urban academic medical center in the Bronx, New York, between March 14 and April 15, 2020, and tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 on reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction assay. Final data collection was April 27, 2020.
Exposures: Patient characteristics, including self-identified ethnicity/race, age, sex, socioeconomic status, and medical comorbidities, were tabulated.
Main outcomes and measures: Overall survival. Associations between patient demographic characteristics, comorbidities, and race/ethnicity were examined using χ2 tests, and the association with survival was assessed using univariable and multivariable Cox proportional hazards regression, based on time from positive COVID-19 test.
Results: Of 9268 patients who were tested, 5902 ethnically diverse patients (63.7%) had SARS-CoV-2. Of these, 3129 patients (53.0%) were women, and the median (interquartile range) age was 58 (44-71) years. A total of 918 patients (15.5%) died within the study time frame. Overall, 1905 patients (32.3%) identified as Hispanic; 1935 (32.8%), non-Hispanic Black; 509 (8.6%), non-Hispanic White; and 171 (2.9%), Asian; the death rates were 16.2% (309), 17.2% (333), 20.0% (102), and 17.0% (29), respectively (P = .25). Hispanic and non-Hispanic Black patients had a higher proportion of more than 2 medical comorbidities with 654 (34.3%) and 764 (39.5%), respectively, compared with 147 (28.9%) among non-Hispanic White patients (P < .001). Hispanic and non-Hispanic Black patients were also more likely to test positive for COVID-19 than White patients, with 1905 of 2919 Hispanic patients (65.3%), 1935 of 2823 non-Hispanic Black patients (68.5%), and 509 of 960 non-Hispanic White patients (53.0%) having positive test results for SARS-CoV-2 (P < .001). While controlling for age, sex, socioeconomic status and comorbidities, patients identifying as Hispanic (hazard ratio, 0.77; 95% CI, 0.61-0.98; P = .03) or non-Hispanic Black (hazard ratio, 0.69; 95% CI, 0.55-0.87; P = .002) had slightly improved survival compared with non-Hispanic White patients.
Conclusions and relevance: In this cohort study of patients with COVID-19 who presented for care at the same urban medical center, non-Hispanic Black and Hispanic patients did not experience worse risk-adjusted outcomes compared with their White counterparts. This finding is important for understanding the observed population differences in mortality by race/ethnicity reported elsewhere.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Racism, Not Race, Drives Inequity Across the COVID-19 Continuum.JAMA Netw Open. 2020 Sep 1;3(9):e2019933. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.19933. JAMA Netw Open. 2020. PMID: 32975568 No abstract available.
References
-
- US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention CDC COVID data tracker. Accessed May 11, 2020. https://www.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/index.html
-
- Richardson S, Hirsch JS, Narasimhan M, et al. ; and the Northwell COVID-19 Research Consortium . Presenting characteristics, comorbidities, and outcomes among 5700 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 in the New York City area. JAMA. 2020;323(20):2052-2059. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.6775 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous