Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor with stenosis of the main pancreatic duct leading to pancreatic pleural effusion: a case report
- PMID: 32975612
- PMCID: PMC7519021
- DOI: 10.1186/s40792-020-00987-7
Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor with stenosis of the main pancreatic duct leading to pancreatic pleural effusion: a case report
Abstract
Background: Pancreatic pleural effusion and ascites are defined as fluid accumulation in the thoracic and abdominal cavity, respectively, due to direct leakage of the pancreatic juice. They usually occur in patients with acute or chronic pancreatitis but are rarely associated with pancreatic neoplasm. We present here an extremely rare case of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor with stenosis of the main pancreatic duct, leading to pancreatic pleural effusion.
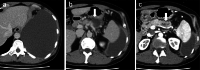
Case presentation: A 51-year-old man complained of dyspnea. Left-sided pleural effusion was detected on the chest X-ray. Pleural puncture was performed, and the pleural fluid indicated a high amylase content (36,854 IU/L). Hence, the patient was diagnosed with pancreatic pleural effusion. Although no tumor was detected, the computed tomography (CT) scan showed a pseudocyst and dilation of the main pancreatic duct in the pancreatic tail. Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography showed a fistula from the pseudocyst into the left thoracic cavity. Endoscopic retrograde pancreatic drainage was attempted; however, it failed due to stenosis in the main pancreatic duct in the pancreatic body. Endoscopic ultrasound revealed a hypoechoic mass measuring 15 × 15 mm in the pancreatic body that was not enhanced in the late phase of contrast perfusion and was thus suspected to be an invasive ductal carcinoma. The patient underwent distal pancreatectomy with splenectomy and the postoperative course was uneventful. Histopathological examination confirmed a neuroendocrine tumor of the pancreas (NET G2). The main pancreatic duct was compressed by the tumor. Increased pressure on the distal pancreatic duct by the tumor might have caused formation of the pseudocyst and pleural effusion. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first case report of pancreatic pleural effusion associated with a neuroendocrine tumor.
Conclusions: Differential diagnosis of a pancreatic neoplasm should be considered, especially when a patient without a history of pancreatitis presents with pleural effusion.
Keywords: Internal pancreatic fistula; Pancreatic ascites; Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor; Pancreatic pleural effusion; Pseudocyst in the pancreatic tail; Stenosis of the main pancreatic duct.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Minimally invasive treatment of an internal pancreaticopleural fistula with massive pleural effusion: a case report.J Med Case Rep. 2024 Sep 15;18(1):430. doi: 10.1186/s13256-024-04761-3. J Med Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 39277749 Free PMC article.
-
Successful treatment of mediastinal pancreatic pseudocyst and pancreatic pleural effusion with endoscopic pancreatic duct drainage: A case report.DEN Open. 2022 Jun 5;3(1):e133. doi: 10.1002/deo2.133. eCollection 2023 Apr. DEN Open. 2022. PMID: 35898838 Free PMC article.
-
[Massive pleural effusion complicating chronic pancreatitis. Treatment by endoscopic closure of a pancreatic-mediastinal fistula].Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 2008 Nov;133(48):2507-9. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1100946. Epub 2008 Nov 19. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 2008. PMID: 19021081 German.
-
[A case of pancreatic carcinoma presenting as pancreaticopleural fistula with pancreatic pleural effusion].Nihon Shokakibyo Gakkai Zasshi. 2010 May;107(5):784-91. Nihon Shokakibyo Gakkai Zasshi. 2010. PMID: 20460853 Review. Japanese.
-
[Pancreatic pleural effusion accompanied by bronchopleural fistula].Nihon Kokyuki Gakkai Zasshi. 1999 Aug;37(8):662-6. Nihon Kokyuki Gakkai Zasshi. 1999. PMID: 10496109 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
The Detection of Immunity against WT1 and SMAD4P130L of EpCAM+ Cancer Cells in Malignant Pleural Effusion.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 12;23(20):12177. doi: 10.3390/ijms232012177. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36293034 Free PMC article.
-
A Rare Case of Isolated Metastasis to the Pleura in the Setting of Newly Diagnosed Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma.J Community Hosp Intern Med Perspect. 2025 Mar 7;15(2):90-93. doi: 10.55729/2000-9666.1454. eCollection 2025. J Community Hosp Intern Med Perspect. 2025. PMID: 40309280 Free PMC article.
-
Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumor (PNET) Presenting as a Pseudocyst: A Case Report.Cureus. 2022 Sep 26;14(9):e29617. doi: 10.7759/cureus.29617. eCollection 2022 Sep. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36320996 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Plockinger U, Rindi G, Arnold R, Eriksson B, Krenning EP, de Herder WW, et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of neuroendocrine gastrointestinal tumours. A consensus statement on behalf of the European Neuroendocrine Tumour Society (ENETS) Neuroendocrinology. 2004;80:394–424. doi: 10.1159/000085237. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Uchiyama T, Suzuki T, Adachi A, Hiraki S, Iizuka N. Pancreatic pleural effusion: case report and review of 113 cases in Japan. Am J Gastroenterol. 1992;87:387–391. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

