Everolimus plus bevacizumab is an effective first-line treatment for patients with advanced papillary variant renal cell carcinoma: Final results from a phase II trial
- PMID: 32975815
- PMCID: PMC8366407
- DOI: 10.1002/cncr.33148
Everolimus plus bevacizumab is an effective first-line treatment for patients with advanced papillary variant renal cell carcinoma: Final results from a phase II trial
Abstract
Background: We previously reported on a phase 2 study of everolimus plus bevacizumab across various nonclear cell renal cell carcinoma (nccRCC) histologies and observed encouraging activity among patients with papillary RCC (pRCC) and unclassified RCC (uRCC) with a major papillary component. We subsequently expanded the study to enroll additional patients with pRCC variants.
Methods: Everolimus plus bevacizumab was administered at standard doses until disease progression or intolerance to therapy. The primary endpoint was the 6-month progression-free survival (PFS) rate; secondary endpoints included objective response rate (ORR), progression-free survival (PFS), overall survival (OS), and safety. Correlative analyses included next-generation sequencing (NGS) from tumor and germline across >341 genes of interest.
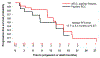
Results: In addition to 19 patients with pRCC variants in the original cohort, 20 patients with similar features were enrolled on the expansion cohort (uRCC with papillary features [n = 24], pRCC [n = 14], and translocation-associated RCC with papillary features [n = 1]). Among 37 evaluable patients, the 6-month PFS rate was 78%, the median PFS was 13.7 months (95% CI, 10.8-16.4 months), and the ORR was 35%. With a median follow-up of 17.6 months, the median OS was 33.9 months (95% CI, 23.3-71.9). Tolerance was consistent with prior reports for everolimus plus bevacizumab. NGS results (n = 33) identified responses in patients with a wide spectrum of genomic alterations, including ARID1A, FH, and MET mutations.
Conclusion: The expansion cohort results confirm robust activity of everolimus plus bevacizumab in metastatic pRCC variants, supporting this regimen as a standard option for this patient population.
Keywords: RCC; bevacizumab; everolimus; genomics; papillary RCC.
© 2020 American Cancer Society.
Figures



References
-
- The American Cancer Society. 2018. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/kidney-cancer/about/key-statistics.html.
-
- Kovacs G, Akhtar M, Beckwith BJ, et al.The Heidelberg classification of renal cell tumours. J Pathol October1997;183(2):131–133. - PubMed
-
- Moch H, Cubilla AL, Humphrey PA, Reuter VE, Ulbright TM. The 2016 WHO Classification of Tumours of the Urinary System and Male Genital Organs-Part A: Renal, Penile, and Testicular Tumours. Eur Urol July2016;70(1):93–105. - PubMed
-
- Vera-Badillo FE, Templeton AJ, Duran I, et al.Systemic therapy for non-clear cell renal cell carcinomas: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Urol April2015;67(4):740–749. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

