Catquest-9SF questionnaire and eCAPS: Validation in a Canadian population
- PMID: 32976522
- PMCID: PMC7518613
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0237788
Catquest-9SF questionnaire and eCAPS: Validation in a Canadian population
Abstract
Background: Visual acuity alone has limitations in assessing a patient's appropriateness and prioritization for cataract surgery. Several tools, including the Catquest-9SF questionnaire and the electronic cataract appropriateness and priority system (eCAPS) have been developed to evaluate patients-reported visual function as related to day-to-day tasks. The aim of this study was to validate Catquest-9SF and eCAPS in a Canadian population and propose a shorter version of each, in an attempt to extend their applicability in clinical practice.
Methods: The English translation of the Swedish Catquest-9SF and eCAPS were self-administered separately in pre-operative patients in tertiary care in Peel region, Ontario. Rasch analysis was used to validate both scales and assess their psychometric properties, such as category threshold order, item fit, unidimensionality, precision, targeting, and differential item functioning.
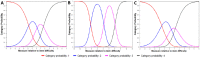
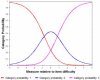
Results: A total of 313 cataract patients (mean age = 69.1, 56.5% female) completed the Catquest-9SF and eCAPS. Catquest-9SF had ordered response thresholds, adequate precision (person separation index = 2.09, person reliability = 0.81), unidimensionality and no misfits (infit range 0.75-1.35, outfit range 0.83-1.36). There mean for patients was equal to -1.43 (lower than the mean for items which is set automatically at zero), meaning that tasks were relatively easy for respondent ability. eCAPS had 3 items that misfit the Rasch model and were excluded (infit range 0.82-1.30, outfit range 0.75-1.36). Precision was inadequate (person separation index = 0.19, person reliability = 0.04). 78.8% of subjects scored≤9 (answered that they had no issues for most questions).
Conclusions: Catquest-9SF demonstrated good psychometric properties and is suitable for assessing visual function of care-seeking patients referred for cataract surgery in Ontario, Canada. There was some mistargeting, suggesting that the tasks were relatively easy to perform, which is consistent with previous research. On the contrary, eCAPS is not sensitive in differentiating patients who had impaired visual functioning.
Conflict of interest statement
IIKA and ML received funding from Alcon Canada Incorporated, Bausch Health Companies Incorporated (formerly Valeant Pharmaceuticals), and Abbot Medical Optics. There are no patents, products in development or marketed products to declare. This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials. There are no other competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Catquest-9SF questionnaire shows greater visual functioning in bilateral cataract populations: A prospective study.Indian J Ophthalmol. 2022 Nov;70(11):3820-3826. doi: 10.4103/ijo.IJO_736_22. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 36308103 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-center validation of Catquest-9SF visual function questionnaire in Ontario, Canada.PLoS One. 2023 Jul 6;18(7):e0278863. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0278863. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37410799 Free PMC article.
-
Catquest-9SF questionnaire: validation of Malay and Chinese-language versions using Rasch analysis.Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2018 Jan 5;16(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s12955-017-0833-3. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2018. PMID: 29304817 Free PMC article.
-
Validation and application of Catquest-9SF in various populations: A systematic review.Surv Ophthalmol. 2020 May-Jun;65(3):348-360. doi: 10.1016/j.survophthal.2019.12.002. Epub 2019 Dec 18. Surv Ophthalmol. 2020. PMID: 31862206
-
[2.6 million cataract surgeries: 31 years with the Swedish National Cataract Register 1992-2022].Lakartidningen. 2024 Feb 14;121:23158. Lakartidningen. 2024. PMID: 38369864 Review. Swedish.
Cited by
-
Catquest-9SF questionnaire shows greater visual functioning in bilateral cataract populations: A prospective study.Indian J Ophthalmol. 2022 Nov;70(11):3820-3826. doi: 10.4103/ijo.IJO_736_22. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 36308103 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting changes in cataract surgery health outcomes using a cataract surgery appropriateness and prioritization instrument.PLoS One. 2021 Jan 28;16(1):e0246104. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0246104. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33507910 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Catquest-9SF questionnaire: Validation in a Greek-speaking population using Rasch analysis.PLoS One. 2022 Dec 7;17(12):e0278683. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0278683. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36477289 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-center validation of Catquest-9SF visual function questionnaire in Ontario, Canada.PLoS One. 2023 Jul 6;18(7):e0278863. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0278863. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37410799 Free PMC article.
-
Validation of the Patient-Reported Outcome Measures Tool "Catquest" in Odia Language.Cureus. 2025 Apr 11;17(4):e82071. doi: 10.7759/cureus.82071. eCollection 2025 Apr. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40357102 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization [Internet]. Blindness and vision impairment; c2019 [cited 2019 July 2]. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/blindness-and-visual-im...
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

