Association of donor IFNL4 genotype and non-relapse mortality after unrelated donor myeloablative haematopoietic stem-cell transplantation for acute leukaemia: a retrospective cohort study
- PMID: 32976751
- PMCID: PMC7735535
- DOI: 10.1016/S2352-3026(20)30294-5
Association of donor IFNL4 genotype and non-relapse mortality after unrelated donor myeloablative haematopoietic stem-cell transplantation for acute leukaemia: a retrospective cohort study
Erratum in
-
Correction to Lancet Haematol 2020; 7: e715-23.Lancet Haematol. 2020 Nov;7(11):e785. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3026(20)30331-8. Lancet Haematol. 2020. PMID: 33091351 No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: The interferon lambda 4 gene (IFNL4) regulates immune responses by controlling the production of IFNλ4, a type III interferon. We hypothesised that IFNλ4 could play a role in infection clearance or alloreactivity in patients with acute leukaemia who received a myeloablative 10/10 HLA-matched haematopoietic stem-cell transplantation (HSCT). Therefore, we aimed to assess the association between recipient and donor IFNL4 genotype with post-HSCT survival outcomes in patients with acute leukaemia.
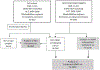
Methods: We did a two-stage retrospective cohort study using the Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research (CIBMTR) repository and database, in which nearly all patients underwent the procedure in the USA. We included patients with acute myeloid leukaemia or acute lymphocytic leukaemia, who received a HSCT at any age from an unrelated 10/10 HLA-matched donor, with a myeloablative conditioning regimen, between Jan 1, 2000, and Dec 31, 2008, and had a pre-HSCT recipient or donor blood sample available. The discovery dataset included patients from an existing National Cancer Institute (NCI) cohort of the CIBMTR database, in which donor and recipient IFNL4 polymorphisms (rs368234815, rs12979860, and rs117648444) were genotyped with TaqMan assays. According to their genotype, donors and recipients were categorised into IFNL4-positive, if they had at least one copy of the allele that supports the production of IFNλ4, or IFNL4-null for the analyses. The findings were independently validated with patients from the DISCOVeRY-BMT cohort (validation dataset) with existing Illumina array genotype data. We also did a combined analysis using data from patients included in both the NCI and DISCOVeRY-BMT cohorts.
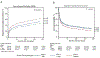
Findings: We assessed 404 patients (who had a HSCT from Jan 9, 2004, to Dec 26, 2008) in the discovery dataset and 1245 patients in the validation dataset (HSCT Jan 7, 2000, to Dec 26, 2008). The combined analysis included 1593 overlapping participants in both cohorts. Donor, but not recipient IFNL4-positive genotype was associated with increased risk of non-relapse mortality (HR 1·60, 95% CI 1·23-2·10; p=0·0005 in the discovery dataset; 1·22, 1·05-1·40; p=0·0072 in the validation dataset; and 1·27, 1·12-1·45; p=0·0001 in the combined dataset). Associations with post-HSCT overall survival were as follows: HR 1·24, 95% CI 1·02-1·51; p=0·034 in the discovery dataset; 1·10, 0·98-1·20; p=0·10 in the validation dataset; and 1·11, 1·02-1·22; p=0·018 in the combined dataset.
Interpretation: Prioritising HSCT donors with the IFNL4-null genotype might decrease non-relapse mortality and improve overall survival without substantially limiting the donor pool. If these findings are validated, IFNL4 genotype could be added to the donor selection algorithm.
Funding: The National Cancer Institute Intramural Research Program. For full funding list see Acknowledgments.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
IFNL4 and donor selection for matched unrelated donor haematopoietic stem-cell transplantation.Lancet Haematol. 2020 Oct;7(10):e698-e699. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3026(20)30287-8. Lancet Haematol. 2020. PMID: 32976742 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Horowitz MM, Gale RP, Sondel PM, et al. Graft-versus-leukemia reactions after bone marrow transplantation. Blood 1990; 75(3): 555–62. - PubMed
-
- Manuel O, Wojtowicz A, Bibert S, et al. Influence of IFNL3/4 polymorphisms on the incidence of cytomegalovirus infection after solid-organ transplantation. J Infect Dis 2015; 211(6): 906–14. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials