Regulation and Roles of the Nucleolus in Embryonic Stem Cells: From Ribosome Biogenesis to Genome Organization
- PMID: 32976768
- PMCID: PMC7724472
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2020.08.012
Regulation and Roles of the Nucleolus in Embryonic Stem Cells: From Ribosome Biogenesis to Genome Organization
Abstract
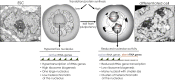
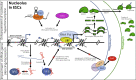
The nucleolus is the largest compartment of the eukaryotic cell's nucleus. It acts as a ribosome factory, thereby sustaining the translation machinery. The nucleolus is also the subnuclear compartment with the highest transcriptional activity in the cell, where hundreds of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) genes transcribe the overwhelming majority of RNAs. The structure and composition of the nucleolus change according to the developmental state. For instance, in embryonic stem cells (ESCs), rRNA genes display a hyperactive transcriptional state and open chromatin structure compared with differentiated cells. Increasing evidence indicates that the role of the nucleolus and rRNA genes might go beyond the control of ribosome biogenesis. One such role is linked to the genome architecture, since repressive domains are often located close to the nucleolus. This review highlights recent findings describing how the nucleolus is regulated in ESCs and its role in regulating ribosome biogenesis and genome organization for the maintenance of stem cell identity.
Keywords: ESCs; NAD; genome organization; hypertranscription; nucleolus; rRNA genes.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genome Organization in and around the Nucleolus.Cells. 2019 Jun 12;8(6):579. doi: 10.3390/cells8060579. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31212844 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nucleolus and rRNA Gene Chromatin in Early Embryo Development.Trends Genet. 2019 Nov;35(11):868-879. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2019.06.005. Epub 2019 Jul 18. Trends Genet. 2019. PMID: 31327501 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging roles for the nucleolus in development and stem cells.Development. 2025 May 1;152(9):dev204696. doi: 10.1242/dev.204696. Epub 2025 May 14. Development. 2025. PMID: 40366093 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nucleolus: the ribosome factory.Histol Histopathol. 2008 Oct;23(10):1291-8. doi: 10.14670/HH-23.1291. Histol Histopathol. 2008. PMID: 18712681 Review.
-
Recent studies implicate the nucleolus as the major site of nuclear translation.Biochem Soc Trans. 2014 Aug;42(4):1224-8. doi: 10.1042/BST20140062. Biochem Soc Trans. 2014. PMID: 25110029 Review.
Cited by
-
Phase Separation: Direct and Indirect Driving Force for High-Order Chromatin Organization.Genes (Basel). 2023 Feb 15;14(2):499. doi: 10.3390/genes14020499. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36833426 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chromatin and Nuclear Architecture in Stem Cells.Stem Cell Reports. 2020 Dec 8;15(6):1155-1157. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2020.11.012. Stem Cell Reports. 2020. PMID: 33296671 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanisms of cellular metabolic homeostasis in stem cells.Int J Oral Sci. 2023 Dec 1;15(1):52. doi: 10.1038/s41368-023-00262-z. Int J Oral Sci. 2023. PMID: 38040705 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Mechanisms of Plant Regeneration from Differentiated Cells: Approaches from Historical Tissue Culture Systems.Plant Cell Physiol. 2023 Mar 15;64(3):297-304. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcac172. Plant Cell Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36546730 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic regulatory layers in the 3D nucleus.Mol Cell. 2024 Feb 1;84(3):415-428. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2023.12.032. Epub 2024 Jan 18. Mol Cell. 2024. PMID: 38242127 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abujarour R., Efe J., Ding S. Genome-wide gain-of-function screen identifies novel regulators of pluripotency. Stem Cells. 2010;28:1487–1497. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

