Preclinical characterization of zuranolone (SAGE-217), a selective neuroactive steroid GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulator
- PMID: 32976892
- PMCID: PMC8265595
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2020.108333
Preclinical characterization of zuranolone (SAGE-217), a selective neuroactive steroid GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulator
Abstract
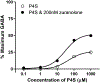
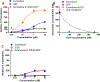
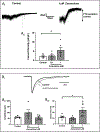
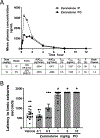
Zuranolone (SAGE-217) is a novel, synthetic, clinical stage neuroactive steroid GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulator designed with the pharmacokinetic properties to support oral daily dosing. In vitro, zuranolone enhanced GABAA receptor current at nine unique human recombinant receptor subtypes, including representative receptors for both synaptic (γ subunit-containing) and extrasynaptic (δ subunit-containing) configurations. At a representative synaptic subunit configuration, α1β2γ2, zuranolone potentiated GABA currents synergistically with the benzodiazepine diazepam, consistent with the non-competitive activity and distinct binding sites of the two classes of compounds at synaptic receptors. In a brain slice preparation, zuranolone produced a sustained increase in GABA currents consistent with metabotropic trafficking of GABAA receptors to the cell surface. In vivo, zuranolone exhibited potent activity, indicating its ability to modulate GABAA receptors in the central nervous system after oral dosing by protecting against chemo-convulsant seizures in a mouse model and enhancing electroencephalogram β-frequency power in rats. Together, these data establish zuranolone as a potent and efficacious neuroactive steroid GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulator with drug-like properties and CNS exposure in preclinical models. Recent clinical data support the therapeutic promise of neuroactive steroid GABAA receptor positive modulators for treating mood disorders; brexanolone is the first therapeutic approved specifically for the treatment of postpartum depression. Zuranolone is currently under clinical investigation for the treatment of major depressive episodes in major depressive disorder, postpartum depression, and bipolar depression.
Keywords: GABA(A) receptor; Neuroactive steroid; Positive allosteric modulator.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests:
All work described in this manuscript was paid for by Sage Therapeutics. Some authors are employees, consultants, or shareholders of Sage Therapeutics.
Figures


References
-
- Althaus AL, McCarren HS, Alqazzaz A, Jackson C, McDonough JH, Smith CD, Hoffman E, Hammond RS, Robichaud AJ, Doherty JJ, 2017. The synthetic neuroactive steroid SGE-516 reduces status epilepticus and neuronal cell death in a rat model of soman intoxication. Epilepsy Behav. 68, 22–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

