The Use of Low-Cost Unmanned Aerial Vehicles in the Process of Building Models for Cultural Tourism, 3D Web and Augmented/Mixed Reality Applications
- PMID: 32977540
- PMCID: PMC7584044
- DOI: 10.3390/s20195457
The Use of Low-Cost Unmanned Aerial Vehicles in the Process of Building Models for Cultural Tourism, 3D Web and Augmented/Mixed Reality Applications
Abstract
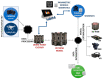
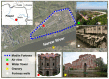
Unmanned Aerial Systems (UAS) are widely used in low-cost photogrammetry. Even small Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAV) can deliver valuable data for the inventory of inaccessible and dangerous areas or objects. The acquisition of data for 3D object modeling is a complicated, time-consuming, and cost-intensive process. It requires the use of expensive equipment and often manual work as well as professional software. These are major barriers limiting the development of modern tourist platforms that promote local attractions. Information technologies offer new opportunities for the development of the services market, including the development of smart tourism services, as an integral part of the smart city concept. 3D models are an important element of this process as they form the basis for the use of new visualization technologies, such as Virtual, Mixed, and Augmented Reality (VR/MR/AR). 3D modeling provides a new opportunity to use AR/MR technology to present information about objects, virtual tours of the historic buildings, and their promotion. It also creates an opportunity to preserve the architectural heritage and preventive maintenance of buildings. Despite the increasing use of new measuring platforms and computer modeling techniques, the implementation of 3D building models in smart tourism services is still limited, focusing more on the results of scientific projects rather than on the implementation of the new ones. The paper presents an universal methodology for the inventory of historical buildings using low-cost UAVs. It describes the most important aspects related to the process of planning UAV measurement missions and photogrammetric data acquisition. The construction of 3D models and the possibilities of their further use to build smart tourism services based on Web/AR/MR/VR technology was also presented.
Keywords: 3D Web; AR; MR; UAV/UAS; cultural heritage; smart city; smart tourism; tourism services.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures














References
-
- Caragliu A., del Bo C., Nijkamp P. Smart cities in Europe. J. Urban Technol. 2011;18:65–82. doi: 10.1080/10630732.2011.601117. - DOI
-
- Camero A., Alba E. Smart City and information technology: A review. Cities. 2019;93:84–94. doi: 10.1016/j.cities.2019.04.014. - DOI
-
- Lamsfus C., Martín D., Alzua-Sorzabal A., Torres-Manzanera E. Smart Tourism Destinations: An Extended Conception of Smart Cities Focusing on Human Mobility. Information and Communication Technologies in Tourism 2015. Springer International Publishing; Cham, Switzerland: 2015. pp. 363–375.
-
- International Organization for Standardization/International Electrotechnical Commission, ISO/IEC Information technology—Security techniques—Information security management systems—Overview and vocabulary. [(accessed on 28 January 2020)]; Available online: http://standards.iso.org/ittf/PubliclyAvailableStandards/c066435_ISO_IEC....
-
- Madirov E., Absalyamova S. The influence of Information Technologies on the Availability of Cultural Heritage. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2015;188:255–258. doi: 10.1016/j.sbspro.2015.03.385. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

