A unique radioprotective effect of resolvin E1 reduces irradiation-induced damage to the inner ear by inhibiting the inflammatory response
- PMID: 32977807
- PMCID: PMC7517621
- DOI: 10.1186/s13014-020-01662-9
A unique radioprotective effect of resolvin E1 reduces irradiation-induced damage to the inner ear by inhibiting the inflammatory response
Abstract
Background: In addition to the direct effects of irradiation, the induced inflammatory response may play an important role in the damage to the inner ear caused by radiotherapy for the treatment of head and neck cancers. Resolvin E1 (RvE1) has anti-inflammatory activity, acting by reducing neutrophil infiltration and proinflammatory cytokine expression. Therefore, in this study we sought to confirm whether the inflammation induced by irradiation was involved in damage to the inner ear after radiotherapy and to investigate the protective effect and underlying mechanism of RvE1 using mouse models.
Methods: A dose of RvE1 was delivered by intraperitoneal injection to mice before irradiation. Changes in the auditory brainstem response (ABR), relative balance ability, inner ear morphology and the expression levels of inflammatory factors in the inner ear were analyzed on days 7 and 14 after irradiation and compared among different experimental groups.
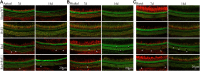
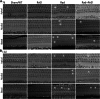
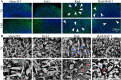
Results: Changes of ABR and relative balance ability showed the inner functions of experimental mice presented severe damage after irradiation, but the damage was significantly alleviated after RvE1 pretreatment compared to irradiation alone. Morphological analysis of the inner ear showed severe damage to the cochlea and vestibule after irradiation. In contrast, damage to the cochlea and vestibule was significantly reduced in the RvE1-pretreated group compared to that in the irradiation alone group. Along with these functional and morphological changes, the mRNA expression level of anti-inflammatory factors interleukin-2 was significantly increased, while those of proinflammatory factors interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-α were significantly decreased in the inner ear of mice after RvE1 pretreatment compared to irradiation alone.
Conclusions: We believe that inflammation induced by irradiation is involved in the damage to the inner ear caused by radiotherapy, and that RvE1 reduces the damage caused by irradiation to the inner ear by regulating the induced inflammatory response.
Keywords: Inflammatory response; Inner ear; Proinflammatory cytokine; Radioprotective effect; Resolvin E1.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Resolvin E1, an endogenous lipid mediator derived from eicosapentaenoic acid, prevents dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis.Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2010 Jan;16(1):87-95. doi: 10.1002/ibd.21029. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2010. PMID: 19572372 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and function of the adult inner ear in the mouse following prenatal irradiation.Scand Audiol Suppl. 1985;24:1-24. Scand Audiol Suppl. 1985. PMID: 3879375
-
Resolvin E1 Regulates Th17 Function and T Cell Activation.Front Immunol. 2021 Mar 17;12:637983. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.637983. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33815391 Free PMC article.
-
The role of polyunsaturated ω-3 fatty acid eicosapentaenoic acid-derived resolvin E1 (RvE1) in bone preservation.Crit Rev Immunol. 2014;34(4):347-57. doi: 10.1615/critrevimmunol.2014009982. Crit Rev Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24941160 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Resolvin E1 as a novel agent for the treatment of asthma.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2009 May;13(5):513-22. doi: 10.1517/14728220902865622. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2009. PMID: 19368495 Review.
Cited by
-
Radiation-induced NF-κB activation is involved in cochlear damage in mice via promotion of a local inflammatory response.J Radiat Res. 2023 Jan 20;64(1):63-72. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rrac068. J Radiat Res. 2023. PMID: 36253086 Free PMC article.
-
High doses of radiation cause cochlear immunological stress and sensorineural hearing loss.Heliyon. 2024 Aug 31;10(18):e37223. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37223. eCollection 2024 Sep 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39309931 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tuan JK, Ha TC, Ong WS, et al. Late toxicities after conventional radiation therapy alone for nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Radiother Oncol. 2012;104(3):305–311. - PubMed
-
- Gamble JE, Peterson EA, Chandler JR. Radiation effects on the inner ear. Arch Otolaryngol. 1968;88(2):156–161. - PubMed
-
- Theunissen EA, Bosma SC, Zuur CL, et al. Sensorineural hearing loss in patients with head and neck cancer after chemoradiotherapy and radiotherapy: a systematic review of the literature. Head Neck. 2015;37(2):281–292. - PubMed
-
- Cooper JS, Pajak TF, Forastiere AA, et al. Postoperative concurrent radiotherapy and chemotherapy for high-risk squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck. N Engl J Med. 2004;350(19):1937–1944. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

