Quantitative examination of video-recorded NHS Health Checks: comparison of the use of QRISK2 versus JBS3 cardiovascular risk calculators
- PMID: 32978197
- PMCID: PMC7520846
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-037790
Quantitative examination of video-recorded NHS Health Checks: comparison of the use of QRISK2 versus JBS3 cardiovascular risk calculators
Abstract
Objectives: Quantitatively examine the content of National Health Service Health Check (NHSHC), patient-practitioner communication balance and differences when using QRISK2 versus JBS3 cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk calculators.
Design: RIsk COmmunication in NHSHC was a qualitative study with quantitative process evaluation, comparing NHSHC using QRISK2 or JBS3. We present data from the quantitative process evaluation.
Setting and participants: Twelve general practices in the West Midlands (England) conducted NHSHC using JBS3 or QRISK2 (6/group). Patients were eligible for NHSHC based on national criteria (aged 40-74, no existing cardiovascular-related diagnoses, not taking statins). Recruitment was stratified by patients' age, gender and ethnicity.
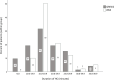
Methods: Video recordings of NHSHC were coded, second-by-second, to quantify who was speaking and what was being discussed. Outcomes included consultation duration, practitioner verbal dominance (ratio of practitioner:patient speaking time (pr:pt ratio)) and proportion of time discussing CVD risk, risk factors and risk management.
Results: 173 video-recorded NHSHC were analysed (73 QRISK, 100 JBS3). The sample was 51% women, 83% white British, with approximately equal proportions across age groups. NHSHC duration varied greatly (6.8-38.0 min). Most (60%) lasted less than 20 min. On average, CVD risk was discussed for less than 2 min (9.06%±4.30% of consultation time). There were indications that, compared with NHSHC using JBS3, those with QRISK2 involved less CVD risk discussion (JBS3 M=10.24%, CI: 8.01-12.48 vs QRISK2 M=7.44%, CI: 5.29-9.58) and were more verbally dominated by practitioners (pr:pt ratio JBS3 M=3.21%, CI: 2.44-3.97 vs QRISK2=2.35%, CI: 1.89-2.81). The largest proportion of NHSHC time was spent discussing causal risk factors (M=37.54%, CI: 32.92-42.17).
Conclusions: There was wide variation in NHSHC duration. Many were short and practitioner-dominated, with little time discussing CVD risk. JBS3 appears to extend CVD risk discussion and patient contribution. Qualitative examination of how it is used is necessary to fully understand the potential benefits of these differences.
Trial registration number: ISRCTN10443908.
Keywords: coronary heart disease; preventive medicine; primary care.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2020. Re-use permitted under CC BY. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
"They are saying it's high, but I think it's quite low": exploring cardiovascular disease risk communication in NHS health checks through video-stimulated recall interviews with patients - a qualitative study.BMC Prim Care. 2024 Apr 23;25(1):126. doi: 10.1186/s12875-024-02357-w. BMC Prim Care. 2024. PMID: 38654245 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiovascular disease risk communication in NHS Health Checks using QRISK®2 and JBS3 risk calculators: the RICO qualitative and quantitative study.Health Technol Assess. 2021 Aug;25(50):1-124. doi: 10.3310/hta25500. Health Technol Assess. 2021. PMID: 34427556
-
A qualitative study of cardiovascular disease risk communication in NHS Health Check using different risk calculators: protocol for the RIsk COmmunication in NHS Health Check (RICO) study.BMC Fam Pract. 2019 Jan 14;20(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s12875-018-0897-0. BMC Fam Pract. 2019. PMID: 30642267 Free PMC article.
-
Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article.
-
What happens after an NHS Health Check? A survey and realist review.Health Soc Care Deliv Res. 2023 Jul;11(12):1-133. doi: 10.3310/RGTH4127. Health Soc Care Deliv Res. 2023. PMID: 37830173 Review.
Cited by
-
A qualitative exploration of two risk calculators using video-recorded NHS health check consultations.BMC Fam Pract. 2020 Dec 3;21(1):250. doi: 10.1186/s12875-020-01315-6. BMC Fam Pract. 2020. PMID: 33272217 Free PMC article.
-
"They are saying it's high, but I think it's quite low": exploring cardiovascular disease risk communication in NHS health checks through video-stimulated recall interviews with patients - a qualitative study.BMC Prim Care. 2024 Apr 23;25(1):126. doi: 10.1186/s12875-024-02357-w. BMC Prim Care. 2024. PMID: 38654245 Free PMC article.
-
Interventions Using Heart Age for Cardiovascular Disease Risk Communication: Systematic Review of Psychological, Behavioral, and Clinical Effects.JMIR Cardio. 2021 Nov 5;5(2):e31056. doi: 10.2196/31056. JMIR Cardio. 2021. PMID: 34738908 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardiovascular disease risk communication in NHS Health Checks: a qualitative video-stimulated recall interview study with practitioners.BJGP Open. 2021 Oct 26;5(5):BJGPO.2021.0049. doi: 10.3399/BJGPO.2021.0049. Print 2021 Oct. BJGP Open. 2021. PMID: 34172476 Free PMC article.
-
NHS Health Check programme: a protocol for a realist review.BMJ Open. 2021 Apr 14;11(4):e048937. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-048937. BMJ Open. 2021. PMID: 33853809 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wilkins E, Wickramasinghe K. European cardiovascular disease statistics 2017 edition. Brussels: European Heart Network, 2017.
-
- National Health Service The NHS long term plan. London: NHS, 2019.
-
- Department of Health and Social Care Advancing our health: prevention in the 2020s – consultation document. London: HMSO, 2019.
-
- Department of Health Putting prevention first. NHS Health Check: vascular risk assessment and management best practice guidance. London: DH, 2009.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials