PFN2 and NAA80 cooperate to efficiently acetylate the N-terminus of actin
- PMID: 32978259
- PMCID: PMC7864067
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.015468
PFN2 and NAA80 cooperate to efficiently acetylate the N-terminus of actin
Abstract
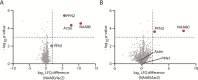
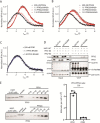
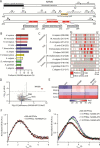
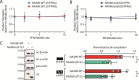
The actin cytoskeleton is of profound importance to cell shape, division, and intracellular force generation. Profilins bind to globular (G-)actin and regulate actin filament formation. Although profilins are well-established actin regulators, the distinct roles of the dominant profilin, profilin 1 (PFN1), versus the less abundant profilin 2 (PFN2) remain enigmatic. In this study, we use interaction proteomics to discover that PFN2 is an interaction partner of the actin N-terminal acetyltransferase NAA80, and further confirm this by analytical ultracentrifugation. Enzyme assays with NAA80 and different profilins demonstrate that PFN2 binding specifically increases the intrinsic catalytic activity of NAA80. NAA80 binds PFN2 through a proline-rich loop, deletion of which abrogates PFN2 binding. Small-angle X-ray scattering shows that NAA80, actin, and PFN2 form a ternary complex and that NAA80 has partly disordered regions in the N-terminus and the proline-rich loop, the latter of which is partly ordered upon PFN2 binding. Furthermore, binding of PFN2 to NAA80 via the proline-rich loop promotes binding between the globular domains of actin and NAA80, and thus acetylation of actin. However, the majority of cellular NAA80 is stably bound to PFN2 and not to actin, and we propose that this complex acetylates G-actin before it is incorporated into filaments. In conclusion, we reveal a functionally specific role of PFN2 as a stable interactor and regulator of the actin N-terminal acetyltransferase NAA80, and establish the modus operandi for NAA80-mediated actin N-terminal acetylation, a modification with a major impact on cytoskeletal dynamics.
Keywords: N-terminal acetyltransferases; NAT; acetylation; actin; cytoskeleton; post-translational modification (PTM); profilin; protein-protein interaction; small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS).
© 2020 Ree et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest—The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Mechanism of actin N-terminal acetylation.Sci Adv. 2020 Apr 8;6(15):eaay8793. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aay8793. eCollection 2020 Apr. Sci Adv. 2020. PMID: 32284999 Free PMC article.
-
N-terminal acetylation of actin by NAA80 is essential for structural integrity of the Golgi apparatus.Exp Cell Res. 2020 May 15;390(2):111961. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2020.111961. Epub 2020 Mar 21. Exp Cell Res. 2020. PMID: 32209306 Free PMC article.
-
Structural determinants and cellular environment define processed actin as the sole substrate of the N-terminal acetyltransferase NAA80.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Apr 24;115(17):4405-4410. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1719251115. Epub 2018 Mar 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 29581307 Free PMC article.
-
Profilin as a dual regulator of actin and microtubule dynamics.Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2020 Mar;77(3-4):76-83. doi: 10.1002/cm.21586. Epub 2019 Dec 17. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2020. PMID: 31811707 Review.
-
Purification of modified mammalian actin isoforms for in vitro reconstitution assays.Eur J Cell Biol. 2023 Dec;102(4):151363. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2023.151363. Epub 2023 Sep 28. Eur J Cell Biol. 2023. PMID: 37778219 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
[Profilin 2 is highly expressed in gastric cancer and promotes tumor cell proliferation and migration].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2022 Feb 20;42(2):215-222. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2022.02.07. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2022. PMID: 35365445 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Biochemical characterization of cardiac α-actin mutations A21V and D26N implicated in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2024 Dec;81(12):815-831. doi: 10.1002/cm.21852. Epub 2024 Mar 9. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2024. PMID: 38459932 Free PMC article.
-
The Final Maturation State of β-actin Involves N-terminal Acetylation by NAA80, not N-terminal Arginylation by ATE1.J Mol Biol. 2022 Jan 30;434(2):167397. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2021.167397. Epub 2021 Dec 9. J Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 34896361 Free PMC article.
-
[LncRNA LINC00342 regulates gastric cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion by targeting miR-596].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2023 Oct 20;43(10):1761-1770. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2023.10.14. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2023. PMID: 37933652 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Naa80 is required for actin N-terminal acetylation and normal hearing in zebrafish.Life Sci Alliance. 2024 Oct 9;7(12):e202402795. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202402795. Print 2024 Dec. Life Sci Alliance. 2024. PMID: 39384430 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

