α2-Macroglobulin-like protein 1 can conjugate and inhibit proteases through their hydroxyl groups, because of an enhanced reactivity of its thiol ester
- PMID: 32978260
- PMCID: PMC7864068
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.015694
α2-Macroglobulin-like protein 1 can conjugate and inhibit proteases through their hydroxyl groups, because of an enhanced reactivity of its thiol ester
Erratum in
-
Correction: α2-Macroglobulin-like protein 1 can conjugate and inhibit proteases through their hydroxyl groups, because of an enhanced reactivity of its thiol ester.J Biol Chem. 2021 Jan-Jun;296:100208. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2020.100208. Epub 2021 Feb 10. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33837737 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
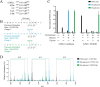
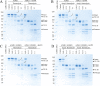
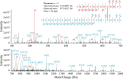
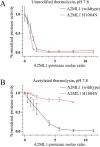
Proteins in the α-macroglobulin (αM) superfamily use thiol esters to form covalent conjugation products upon their proteolytic activation. αM protease inhibitors use theirs to conjugate proteases and preferentially react with primary amines (e.g. on lysine side chains), whereas those of αM complement components C3 and C4B have an increased hydroxyl reactivity that is conveyed by a conserved histidine residue and allows conjugation to cell surface glycans. Human α2-macroglobulin-like protein 1 (A2ML1) is a monomeric protease inhibitor but has the hydroxyl reactivity-conveying histidine residue. Here, we have investigated the role of hydroxyl reactivity in a protease inhibitor by comparing recombinant WT A2ML1 and the A2ML1 H1084N mutant in which this histidine is removed. Both of A2ML1s' thiol esters were reactive toward the amine substrate glycine, but only WT A2ML1 reacted with the hydroxyl substrate glycerol, demonstrating that His-1084 increases the hydroxyl reactivity of A2ML1's thiol ester. Although both A2ML1s conjugated and inhibited thermolysin, His-1084 was required for the conjugation and inhibition of acetylated thermolysin, which lacks primary amines. Using MS, we identified an ester bond formed between a thermolysin serine residue and the A2ML1 thiol ester. These results demonstrate that a histidine-enhanced hydroxyl reactivity can contribute to protease inhibition by an αM protein. His-1084 did not improve A2ML1's protease inhibition at pH 5, indicating that A2ML1's hydroxyl reactivity is not an adaption to its acidic epidermal environment.
Keywords: A2ML1; alpha 2 macroglobulin like protein 1; alpha-2-macroglobulin; complement; inhibition mechanism; mutagenesis; mutagenesis in vitro; protease; protease inhibitor; protein crosslinking; thiol ester; α2-macroglobulin.
© 2020 Harwood et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest—The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cryo-EM structures of human A2ML1 elucidate the protease-inhibitory mechanism of the A2M family.Nat Commun. 2022 May 31;13(1):3033. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-30758-x. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35641520 Free PMC article.
-
A novel protease inhibitor of the alpha2-macroglobulin family expressed in the human epidermis.J Biol Chem. 2006 Mar 3;281(9):5780-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M508017200. Epub 2005 Nov 18. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16298998
-
Interaction of mannan binding lectin with alpha2 macroglobulin via exposed oligomannose glycans: a conserved feature of the thiol ester protein family?J Biol Chem. 2006 Mar 17;281(11):6955-63. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M511432200. Epub 2006 Jan 5. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16407218
-
Invertebrate alpha 2-macroglobulin: structure-function and the ancient thiol ester bond.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1994 Apr 15;712:131-45. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1994.tb33568.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1994. PMID: 7514851 Review. No abstract available.
-
The phylogeny and evolution of the thioester bond-containing proteins C3, C4 and alpha 2-macroglobulin.Immunol Rev. 1998 Dec;166:15-26. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1998.tb01249.x. Immunol Rev. 1998. PMID: 9914899 Review.
Cited by
-
Engineering New Protease Inhibitors Using α2-Macroglobulin.Methods Mol Biol. 2024;2747:279-294. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3589-6_21. Methods Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38038947
-
Multi-omics integration and machine learning uncover molecular basal-like subtype of pancreatic cancer and implicate A2ML1 in promoting tumor epithelial-mesenchymal transition.J Transl Med. 2025 Jul 4;23(1):741. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06711-z. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40615919 Free PMC article.
-
Cryo-EM structures of human A2ML1 elucidate the protease-inhibitory mechanism of the A2M family.Nat Commun. 2022 May 31;13(1):3033. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-30758-x. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35641520 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Numata S., Teye K., Tsuruta D., Sogame R., Ishii N., Koga H., Natsuaki Y., Tsuchisaka A., Hamada T., Karashima T., Nakama T., Furumura M., Ohata C., Kawakami T., Schepens I. Anti-alpha-2-macroglobulin-like-1 autoantibodies are detected frequently and may be pathogenic in paraneoplastic pemphigus. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2013;133:1785–1793. doi: 10.1038/jid.2013.65. 23407400. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Larson E.D., Magno J.P.M., Steritz M.J., Llanes E., Cardwell J., Pedro M., Roberts T.B., Einarsdottir E., Rosanes R.A.Q., Greenlee C., Santos R.A.P., Yousaf A., Streubel S.O., Santos A.T.R., Ruiz A.G. A2ML1 and otitis media: Novel variants, differential expression, and relevant pathways. Hum. Mutat. 2019;40:1156–1171. doi: 10.1002/humu.23769. 31009165. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Santos-Cortez R.L., Chiong C.M., Reyes-Quintos M.R., Tantoco M.L., Wang X., Acharya A., Abbe I., Giese A.P., Smith J.D., Allen E.K., Li B., Cutiongco-de la Paz E.M., Garcia M.C., Llanes E.G., Labra P.J. Rare A2ML1 variants confer susceptibility to otitis media. Nat. Genet. 2015;47:917–920. doi: 10.1038/ng.3347. 26121085. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Caubet C., Jonca N., Brattsand M., Guerrin M., Bernard D., Schmidt R., Egelrud T., Simon M., Serre G. Degradation of corneodesmosome proteins by two serine proteases of the kallikrein family, SCTE/KLK5/hK5 and SCCE/KLK7/hK7. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2004;122:1235–1244. doi: 10.1111/j.0022-202X.2004.22512.x. 15140227. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

