The miR-361-3p increases enzalutamide (Enz) sensitivity via targeting the ARv7 and MKNK2 to better suppress the Enz-resistant prostate cancer
- PMID: 32978369
- PMCID: PMC7519644
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-020-02932-w
The miR-361-3p increases enzalutamide (Enz) sensitivity via targeting the ARv7 and MKNK2 to better suppress the Enz-resistant prostate cancer
Abstract
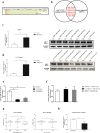
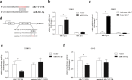
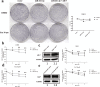
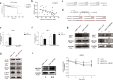
The androgen receptor splicing variant 7 (ARv7) that lacks the ligand-binding domain is increasingly considered as a key player leading to enzalutamide (Enz) resistance in patients with prostate cancer (PCa). However, the detailed mechanisms of how ARv7 expression is regulated and whether it also needs other factors to induce maximal Enz resistance remain unclear. Here, we identified a microRNA, miR-361-3p, whose expression is lower in patients with recurrent PCa, could function via binding to the 3'UTR of ARv7, but not the wild type of AR, to suppress its expression to increase the Enz sensitivity. Importantly, we found that miR-361-3p could also bind to the 3'UTR of MAP kinase-interacting serine/threonine kinase 2 (MKNK2) to suppress its expression to further increase the Enz sensitivity. In turn, the increased Enz can then function via a feedback mechanism through altering the HIF-2α/VEGFA signaling to suppress the expression of miR-361-3p under hypoxia conditions. Preclinical studies using an in vivo mouse model with orthotopically xenografted CWR22Rv1 cells demonstrated that combining the Enz with the small molecule miR-361-3p would result in better suppression of the Enz-resistant PCa tumor progression. Together, these preclinical studies demonstrate that miR-361-3p can function via suppressing the expression of ARv7 and MKNK2 to maximally increase the Enz sensitivity, and targeting these newly identified Enz/miR-361-3p/ARv7 and/or Enz/miR-361-3p/MKNK2 signals with small molecules may help in the development of novel therapies to better suppress the CRPC in patients that already have developed the Enz resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Preclinical studies using cisplatin/carboplatin to restore the Enzalutamide sensitivity via degrading the androgen receptor splicing variant 7 (ARv7) to further suppress Enzalutamide resistant prostate cancer.Cell Death Dis. 2020 Nov 2;11(11):942. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-02970-4. Cell Death Dis. 2020. PMID: 33139720 Free PMC article.
-
Preclinical study using circular RNA 17 and micro RNA 181c-5p to suppress the enzalutamide-resistant prostate cancer progression.Cell Death Dis. 2019 Jan 15;10(2):37. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-1048-1. Cell Death Dis. 2019. PMID: 30674872 Free PMC article.
-
Natural killer cells suppress enzalutamide resistance and cell invasion in the castration resistant prostate cancer via targeting the androgen receptor splicing variant 7 (ARv7).Cancer Lett. 2017 Jul 10;398:62-69. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2017.03.035. Epub 2017 Mar 31. Cancer Lett. 2017. PMID: 28373004
-
The mechanism of histone modifications in regulating enzalutamide sensitivity in advanced prostate cancer.Int J Biol Sci. 2025 Apr 13;21(6):2880-2890. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.109638. eCollection 2025. Int J Biol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40303302 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of BioResponse 3,3'-Diindolylmethane in the Treatment of Human Prostate Cancer: Clinical Experience.Med Princ Pract. 2016;25 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):11-7. doi: 10.1159/000439307. Epub 2015 Oct 27. Med Princ Pract. 2016. PMID: 26501150 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Androgen Receptor-Related Non-coding RNAs in Prostate Cancer.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Apr 1;9:660853. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.660853. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33869227 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of circ_0058357 as a regulator in non-small cell lung cancer cells resistant to cisplatin by miR-361-3p/ABCC1 axis.Thorac Cancer. 2021 Nov;12(21):2894-2906. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.14150. Epub 2021 Sep 14. Thorac Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34523261 Free PMC article.
-
Hsa_circ_0011385 knockdown represses cell proliferation in hepatocellular carcinoma.Cell Death Discov. 2021 Oct 1;7(1):270. doi: 10.1038/s41420-021-00664-0. Cell Death Discov. 2021. PMID: 34599150 Free PMC article.
-
Long noncoding RNA BBOX1-AS1 promotes the progression of gastric cancer by regulating the miR-361-3p/Mucin 13 signaling axis.Bioengineered. 2022 May;13(5):13407-13421. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2072629. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 36700475 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA BBOX1-AS1 Contributes to the Progression of Esophageal Carcinoma by Targeting the miR-361-3p/COL5A1 Axis.Biochem Genet. 2023 Aug;61(4):1351-1368. doi: 10.1007/s10528-022-10307-3. Epub 2022 Dec 31. Biochem Genet. 2023. PMID: 36586008
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

