Comparative analysis of rhizosphere soil physiochemical characteristics and microbial communities between rusty and healthy ginseng root
- PMID: 32978430
- PMCID: PMC7519692
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-71024-8
Comparative analysis of rhizosphere soil physiochemical characteristics and microbial communities between rusty and healthy ginseng root
Abstract
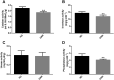
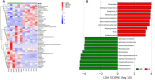
Ginseng rusty root (GRR) symptom is one of the primary diseases of ginseng. There has been a problem of ginseng rusty root, leading to a severe decline in the quality of ginseng. To clarify the relationship between root symptoms of ginseng rust and soil, the physical and chemical properties, enzyme activity, community structure and microbial diversity of GRR and healthy ginseng (HG) rhizosphere soil were analyzed and compared. The pH and redox potential (Eh) of GRR soil decreased, and the contents of total phosphorus (TP), available phosphorus (AP), and available potassium (AK) decreased. The activity of catalase and phosphatase and invertase was lower than that of HG groups. Besides, the microbial community of GRR rhizosphere soil changes much, and its abundance and diversity are significantly reduced. The community structure of GRR rhizosphere soil also shows apparent differences, and the samples of the HG group gathered together, and the samples of the GRR group were dispersed. In general, GRR was closely associated with decreases in soil pH and Eh; decreases in TP, AP, and AK; decreases in the activity of several enzymes. Additionally, it is strongly associated with an increase in pathogenic microorganisms such as Ilyonectria and a reduction of beneficial microorganisms such as Tremellomycetes Acidobacteria subgroup 6 and Gemmatimonadetes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




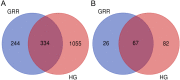


Similar articles
-
The discovery of pivotal fungus and major determinant factor shaping soil microbial community composition associated with rot root of American ginseng.Plant Signal Behav. 2021 Nov 2;16(11):1952372. doi: 10.1080/15592324.2021.1952372. Epub 2021 Jul 25. Plant Signal Behav. 2021. PMID: 34304705 Free PMC article.
-
Rhizosphere analysis of field-grown Panax ginseng with different degrees of red skin provides the basis for preventing red skin syndrome.BMC Microbiol. 2022 Jan 6;22(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s12866-021-02430-9. BMC Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 34991491 Free PMC article.
-
Microbial Community Changes in the Rhizosphere Soil of Healthy and Rusty Panax ginseng and Discovery of Pivotal Fungal Genera Associated with Rusty Roots.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Jan 15;2020:8018525. doi: 10.1155/2020/8018525. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32016120 Free PMC article.
-
[Progress in improvement of continuous monoculture cropping problem in Panax ginseng by controlling soil-borne disease management].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2016 Nov;41(21):3890-3896. doi: 10.4268/cjcmm20162102. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 28929671 Review. Chinese.
-
The Rhizosphere Microbiome of Ginseng.Microorganisms. 2022 Jun 2;10(6):1152. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10061152. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 35744670 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The discovery of pivotal fungus and major determinant factor shaping soil microbial community composition associated with rot root of American ginseng.Plant Signal Behav. 2021 Nov 2;16(11):1952372. doi: 10.1080/15592324.2021.1952372. Epub 2021 Jul 25. Plant Signal Behav. 2021. PMID: 34304705 Free PMC article.
-
Beneficial Soil Fungus Kills Predatory Nematodes with Dehydropeptides Translocating into the Animal Gut.J Am Chem Soc. 2024 Dec 18;146(50):34702-34710. doi: 10.1021/jacs.4c12989. Epub 2024 Dec 9. J Am Chem Soc. 2024. PMID: 39652677 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of ginseng rusty root symptoms transcriptome and its pathogenesis directed by reactive oxygen species theory.Plant Direct. 2024 May 17;8(5):e586. doi: 10.1002/pld3.586. eCollection 2024 May. Plant Direct. 2024. PMID: 38766510 Free PMC article.
-
Commonalities between the Atacama Desert and Antarctica rhizosphere microbial communities.Front Microbiol. 2023 Jul 19;14:1197399. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1197399. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37538842 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of genotype and ecological environment on the community structure and function of symbiotic bacteria in rhizosphere of ginseng.BMC Microbiol. 2022 Oct 3;22(1):235. doi: 10.1186/s12866-022-02649-0. BMC Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36192685 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

