Whey protein isolate inhibits hepatic FGF21 production, which precedes weight gain, hyperinsulinemia and hyperglycemia in mice fed a high-fat diet
- PMID: 32978487
- PMCID: PMC7519058
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-72975-8
Whey protein isolate inhibits hepatic FGF21 production, which precedes weight gain, hyperinsulinemia and hyperglycemia in mice fed a high-fat diet
Abstract
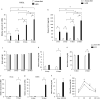
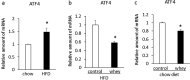
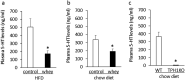
Insufficient expression of hepatic fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) and stromal cell-derived factor 2 like 1 (Sdf2l1) reportedly leads to insulin resistance and hepatosteatosis in obesity and type 2 diabetes. On the other hand, increased expression of hepatic serotonin receptor 2a (htr2a) in diet-induced obesity contributes to hepatosteatosis. Here we show that increases in circulating FGF21 levels and expression of hepatic FGF21 preceded weight gain, hyperinsulinemia, and hyperglycemia in C57BLJ6 mice fed a high-fat diet. Expression of hepatic htr2a and Sdf2l1 increased in insulin-resistant mice fed a high-fat diet. Intake of whey protein isolate decreased plasma FGF21 levels and expression of hepatic FGF21 in mice fed either a high-fat diet or a chow diet, whereas it only suppressed the overexpression of hepatic Sdf2 and htr2a in insulin-resistant mice fed a high-fat diet. Moreover, intake of whey protein isolate decreased plasma serotonin levels in mice fed either a high-fat diet or a chow diet. Genetic inhibition of tryptophan hydroxylase 1 decreased hepatic FGF21 expression and plasma FGF21 levels in mice. These findings suggest that increased hepatic FGF21 production precedes diet-induced weight gain, hyperinsulinemia, and hyperglycemia, and that intake of whey protein isolate could inhibit hepatic FGF21 production by suppressing peripheral serotonin synthesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

