Management of odontogenic infections and sepsis: an update
- PMID: 32978579
- PMCID: PMC7517749
- DOI: 10.1038/s41415-020-2114-5
Management of odontogenic infections and sepsis: an update
Abstract
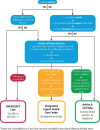
The management of odontogenic infections has improved over recent decades, but further improvements are still required. The ongoing education of GDPs and their dental teams on this issue continues to be important, especially during the current COVID-19 pandemic, where remote triage poses additional difficulties and challenges.Odontogenic infections can lead to sepsis, a potentially life-threatening condition caused by the body's immune system responding in an abnormal way. This can lead to tissue damage, organ failure and death. A patient with non-odontogenic-related infection could also present with sepsis at a dental practice. Early recognition and prompt management of sepsis improves outcomes. GDPs and their dental teams should be trained in the recognition and management of sepsis. Age-specific sepsis decision support tools have been developed by the UK Sepsis Trust to help dental staff recognise and manage patients with suspected sepsis.The aim of this article is to provide an update on the management of odontogenic infections and sepsis.
Figures




Comment in
-
Three things.Br Dent J. 2020 Dec;229(11):701. doi: 10.1038/s41415-020-2464-z. Br Dent J. 2020. PMID: 33311660 No abstract available.
-
Tips for odontogenic infections.Br Dent J. 2020 Dec;229(12):760-761. doi: 10.1038/s41415-020-2516-4. Br Dent J. 2020. PMID: 33339909 No abstract available.
References
-
- SDCEP. Drugs for the Management of Dental Problems During COVID-19 Pandemic. 2020. Available at https://www.sdcep.org.uk/wp-content/uploads/2020/05/SDCEP-MADP-COVID-19-... (accessed May 2020).
-
- SDCEP.Management of Acute Dental Problems During COVID-19 Pandemic. 2020. Available at https://www.sdcep.org.uk/wp-content/uploads/2020/03/SDCEP-MADP-COVID-19-... (accessed May 2020).
-
- Gilway D, Brown S J. Medical emergencies: Sepsis in primary dental care. Br Dent J 2016; 220: 278. - PubMed
-
- UK Sepsis Trust. Professional resources. 2020. Available online at https://sepsistrust.org/professional-resources/ (accessed May 2020).
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

