Therapeutic Potential of Senolytics in Cardiovascular Disease
- PMID: 32979174
- PMCID: PMC8770386
- DOI: 10.1007/s10557-020-07075-w
Therapeutic Potential of Senolytics in Cardiovascular Disease
Abstract
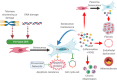
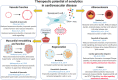
Ageing is the biggest risk factor for impaired cardiovascular health, with cardiovascular disease being the leading cause of death in 40% of individuals over 65 years old. Ageing is associated with both an increased prevalence of cardiovascular disease including heart failure, coronary artery disease, and myocardial infarction. Furthermore, ageing is associated with a poorer prognosis to these diseases. Genetic models allowing the elimination of senescent cells revealed that an accumulation of senescence contributes to the pathophysiology of cardiovascular ageing and promotes the progression of cardiovascular disease through the expression of a proinflammatory and profibrotic senescence-associated secretory phenotype. These studies have resulted in an effort to identify pharmacological therapeutics that enable the specific elimination of senescent cells through apoptosis induction. These senescent cell apoptosis-inducing compounds are termed senolytics and their potential to ameliorate age-associated cardiovascular disease is the focus of this review.
Keywords: Atherosclerosis; Cardiovascular; Inflammation; Remodelling; Senescence; Senolytic.
© 2020. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

