History of the Plague: An Ancient Pandemic for the Age of COVID-19
- PMID: 32979306
- PMCID: PMC7513766
- DOI: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2020.08.019
History of the Plague: An Ancient Pandemic for the Age of COVID-19
Abstract
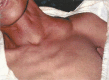
During the fourteenth century, the bubonic plague or Black Death killed more than one third of Europe or 25 million people. Those afflicted died quickly and horribly from an unseen menace, spiking high fevers with suppurative buboes (swellings). Its causative agent is Yersinia pestis, creating recurrent plague cycles from the Bronze Age into modern-day California and Mongolia. Plague remains endemic in Madagascar, Congo, and Peru. This history of medicine review highlights plague events across the centuries. Transmission is by fleas carried on rats, although new theories include via human body lice and infected grain. We discuss symptomatology and treatment options. Pneumonic plague can be weaponized for bioterrorism, highlighting the importance of understanding its clinical syndromes. Carriers of recessive familial Mediterranean fever (FMF) mutations have natural immunity against Y. pestis. During the Black Death, Jews were blamed for the bubonic plague, perhaps because Jews carried FMF mutations and died at lower plague rates than Christians. Blaming minorities for epidemics echoes across history into our current coronavirus pandemic and provides insightful lessons for managing and improving its outcomes.
Keywords: Bioterrorism; Black Death; Bubonic plague; COVID-19; Evolutionary adaptation; Familial Mediterranean fever (FMF); Pneumonic plague; Pyrin; Yersinia pestis.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Benedictow OJ. Boydell Press; Woodbridge, UK: 2004. The Black Death 1346-1353. The Complete History; pp. 3–67.
-
- Kelly J. HarperCollins; New York, NY: 2006. The Great Mortality. An Intimate History of the Black Death, the Most Devastating Plague of All Time; pp. 138–141. 1-77.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

