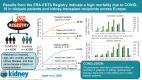
Results from the ERA-EDTA Registry indicate a high mortality due to COVID-19 in dialysis patients and kidney transplant recipients across Europe
- PMID: 32979369
- PMCID: PMC7560263
- DOI: 10.1016/j.kint.2020.09.006
Results from the ERA-EDTA Registry indicate a high mortality due to COVID-19 in dialysis patients and kidney transplant recipients across Europe
Abstract
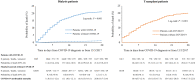
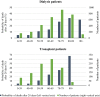
The aim of this study was to investigate 28-day mortality after COVID-19 diagnosis in the European kidney replacement therapy population. In addition, we determined the role of patient characteristics, treatment factors, and country on mortality risk with the use of ERA-EDTA Registry data on patients receiving kidney replacement therapy in Europe from February 1, 2020, to April 30, 2020. Additional data on all patients with a diagnosis of COVID-19 were collected from 7 European countries encompassing 4298 patients. COVID-19-attributable mortality was calculated using propensity score-matched historic control data and after 28 days of follow-up was 20.0% (95% confidence interval 18.7%-21.4%) in 3285 patients receiving dialysis and 19.9% (17.5%-22.5%) in 1013 recipients of a transplant. We identified differences in COVID-19 mortality across countries, and an increased mortality risk in older patients receiving kidney replacement therapy and male patients receiving dialysis. In recipients of kidney transplants ≥75 years of age, 44.3% (35.7%-53.9%) did not survive COVID-19. Mortality risk was 1.28 (1.02-1.60) times higher in transplant recipients compared with matched dialysis patients. Thus, the pandemic has had a substantial effect on mortality in patients receiving kidney replacement therapy, a highly vulnerable population due to underlying chronic kidney disease and a high prevalence of multimorbidity.
Keywords: COVID-19; attributable mortality; dialysis; kidney replacement therapy; registries; transplantation.
Copyright © 2020 International Society of Nephrology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control COVID-19 situation update for the EU/EEA and the UK. https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/cases-2019-ncov-eueea Available at:
-
- Wu Z., McGoogan J.M. Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. JAMA. 2020;323:1239–1242. - PubMed
-
- de Jager D.J., Grootendorst D.C., Jager K.J. Cardiovascular and noncardiovascular mortality among patients starting dialysis. JAMA. 2009;302:1782–1789. - PubMed
-
- ERA-EDTA Registry ERA-EDTA Registry Annual Report 2017. 2019. https://www.era-edta.org/en/registry/publications/annual-reports/#2017 Available at:
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

