Evasion of Type I Interferon by SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 32979938
- PMCID: PMC7501843
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108234
Evasion of Type I Interferon by SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
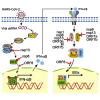
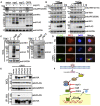
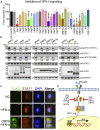
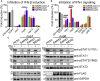
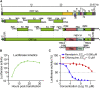
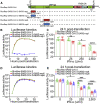
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) replication and host immune response determine coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), but studies evaluating viral evasion of immune response are lacking. Here, we use unbiased screening to identify SARS-CoV-2 proteins that antagonize type I interferon (IFN-I) response. We found three proteins that antagonize IFN-I production via distinct mechanisms: nonstructural protein 6 (nsp6) binds TANK binding kinase 1 (TBK1) to suppress interferon regulatory factor 3 (IRF3) phosphorylation, nsp13 binds and blocks TBK1 phosphorylation, and open reading frame 6 (ORF6) binds importin Karyopherin α 2 (KPNA2) to inhibit IRF3 nuclear translocation. We identify two sets of viral proteins that antagonize IFN-I signaling through blocking signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 (STAT1)/STAT2 phosphorylation or nuclear translocation. Remarkably, SARS-CoV-2 nsp1 and nsp6 suppress IFN-I signaling more efficiently than SARS-CoV and Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV). Thus, when treated with IFN-I, a SARS-CoV-2 replicon replicates to a higher level than chimeric replicons containing nsp1 or nsp6 from SARS-CoV or MERS-CoV. Altogether, the study provides insights on SARS-CoV-2 evasion of IFN-I response and its potential impact on viral transmission and pathogenesis.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; coronavirus disease 2019; immune evasion; interferon; replicon; severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Assiri A., Al-Tawfiq J.A., Al-Rabeeah A.A., Al-Rabiah F.A., Al-Hajjar S., Al-Barrak A., Flemban H., Al-Nassir W.N., Balkhy H.H., Al-Hakeem R.F., et al. Epidemiological, demographic, and clinical characteristics of 47 cases of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus disease from Saudi Arabia: a descriptive study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2013;13:752–761. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Balachandran S., Roberts P.C., Brown L.E., Truong H., Pattnaik A.K., Archer D.R., Barber G.N. Essential role for the dsRNA-dependent protein kinase PKR in innate immunity to viral infection. Immunity. 2000;13:129–141. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

