Gabapentin for chronic pelvic pain in women (GaPP2): a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial
- PMID: 32979978
- PMCID: PMC7527829
- DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31693-7
Gabapentin for chronic pelvic pain in women (GaPP2): a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial
Erratum in
-
Department of Error.Lancet. 2020 Oct 24;396(10259):1334. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32159-0. Lancet. 2020. PMID: 34338213 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Chronic pelvic pain affects 2-24% of women worldwide and evidence for medical treatments is scarce. Gabapentin is effective in treating some chronic pain conditions. We aimed to measure the efficacy and safety of gabapentin in women with chronic pelvic pain and no obvious pelvic pathology.
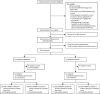
Methods: We performed a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled randomised trial in 39 UK hospital centres. Eligible participants were women with chronic pelvic pain (with or without dysmenorrhoea or dyspareunia) of at least 3 months duration. Inclusion criteria were 18-50 years of age, use or willingness to use contraception to avoid pregnancy, and no obvious pelvic pathology at laparoscopy, which must have taken place at least 2 weeks before consent but less than 36 months previously. Participants were randomly assigned in a 1:1 ratio to receive gabapentin (titrated to a maximum dose of 2700 mg daily) or matching placebo for 16 weeks. The online randomisation system minimised allocations by presence or absence of dysmenorrhoea, psychological distress, current use of hormonal contraceptives, and hospital centre. The appearance, route, and administration of the assigned intervention were identical in both groups. Patients, clinicians, and research staff were unaware of the trial group assignments throughout the trial. Participants were unmasked once they had provided all outcome data at week 16-17, or sooner if a serious adverse event requiring knowledge of the study drug occurred. The dual primary outcome measures were worst and average pain scores assessed separately on a numerical rating scale in weeks 13-16 after randomisation, in the intention-to-treat population. Self-reported adverse events were assessed according to intention-to-treat principles. This trial is registered with the ISRCTN registry, ISCRTN77451762.
Findings: Participants were screened between Nov 30, 2015, and March 6, 2019, and 306 were randomly assigned (153 to gabapentin and 153 to placebo). There were no significant between-group differences in both worst and average numerical rating scale (NRS) pain scores at 13-16 weeks after randomisation. The mean worst NRS pain score was 7·1 (standard deviation [SD] 2·6) in the gabapentin group and 7·4 (SD 2·2) in the placebo group. Mean change from baseline was -1·4 (SD 2·3) in the gabapentin group and -1·2 (SD 2·1) in the placebo group (adjusted mean difference -0·20 [97·5% CI -0·81 to 0·42]; p=0·47). The mean average NRS pain score was 4·3 (SD 2·3) in the gabapentin group and 4·5 (SD 2·2) in the placebo group. Mean change from baseline was -1·1 (SD 2·0) in the gabapentin group and -0·9 (SD 1·8) in the placebo group (adjusted mean difference -0·18 [97·5% CI -0·71 to 0·35]; p=0·45). More women had a serious adverse event in the gabapentin group than in the placebo group (10 [7%] of 153 in the gabapentin group compared with 3 [2%] of 153 in the placebo group; p=0·04). Dizziness, drowsiness, and visual disturbances were more common in the gabapentin group.
Interpretation: This study was adequately powered, but treatment with gabapentin did not result in significantly lower pain scores in women with chronic pelvic pain, and was associated with higher rates of side-effects than placebo. Given the increasing reports of abuse and evidence of potential harms associated with gabapentin use, it is important that clinicians consider alternative treatment options to off-label gabapentin for the management of chronic pelvic pain and no obvious pelvic pathology.
Funding: National Institute for Health Research.
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd. This is an Open Access article under the CC BY 4.0 license. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Zondervan KT, Yudkin PL, Vessey MP, Dawes MG, Barlow DH, Kennedy SH. Prevalence and incidence of chronic pelvic pain in primary care: evidence from a national general practice database. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1999;106:1149–1155. - PubMed
-
- Daniels JP, Khan KS. Chronic pelvic pain in women. BMJ. 2010;341 - PubMed
-
- Horne AW, Vincent K, Cregg R, Daniels J. Is gabapentin effective for women with unexplained chronic pelvic pain? BMJ. 2017;358 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

