Natural history of SARS-CoV-2 infection in healthcare workers in Northern Italy
- PMID: 32980489
- PMCID: PMC7833944
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jhin.2020.08.027
Natural history of SARS-CoV-2 infection in healthcare workers in Northern Italy
Abstract
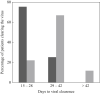
At present, the time-frame used for the quarantine of individuals with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is the entire duration of symptoms plus 14 days after symptom recovery; however, no data have been reported specifically for healthcare workers (HCWs). In the study population of 142 HCWs with COVID-19, the mean time for viral clearance was 31.8 days. Asymptomatic subjects cleared the virus more quickly than symptomatic subjects (22 vs 34.2 days; P<0.0001). The presence of fever at the time of diagnosis was associated with a longer time to viral clearance (relative risk 11.45, 95% confidence interval 8.66-14.25; P<0.0001). These findings may have a significant impact on healthcare strategies for the future management of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Copyright © 2020 The Healthcare Infection Society. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Transmission of infection from non-isolated patients with COVID-19 to healthcare workers.J Hosp Infect. 2020 Dec;106(4):639-642. doi: 10.1016/j.jhin.2020.08.015. Epub 2020 Aug 20. J Hosp Infect. 2020. PMID: 32828865 Free PMC article.
-
Inappropriate risk perception for SARS-CoV-2 infection among Italian HCWs in the eve of COVID-19 pandemic.Acta Biomed. 2020 May 14;91(3):e2020040. doi: 10.23750/abm.v91i3.9727. Acta Biomed. 2020. PMID: 32921735 Free PMC article.
-
Containment of a Large SARS-CoV-2 Outbreak Among Healthcare Workers in a Pediatric Intensive Care Unit.Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2020 Nov;39(11):e336-e339. doi: 10.1097/INF.0000000000002866. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2020. PMID: 32826719
-
Guidance for otolaryngology health care workers performing aerosol generating medical procedures during the COVID-19 pandemic.J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020 Jun 3;49(1):36. doi: 10.1186/s40463-020-00429-2. J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020. PMID: 32493489 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID19: A Systematic Approach to Early Identification and Healthcare Worker Protection.Front Public Health. 2020 May 19;8:205. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2020.00205. eCollection 2020. Front Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32574296 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Insight into the reason of prolonged viral RNA shedding in patients with COVID-19 infection.J Infect. 2021 Apr;82(4):e13-e14. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2020.12.030. Epub 2021 Jan 3. J Infect. 2021. PMID: 33406394 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
PTSD and Depression in Healthcare Workers in the Italian Epicenter of the COVID-19 Outbreak.Clin Pract Epidemiol Ment Health. 2021 Dec 24;17:242-252. doi: 10.2174/1745017902117010242. eCollection 2021. Clin Pract Epidemiol Ment Health. 2021. PMID: 35173794 Free PMC article.
-
Viral Clearance Course of COVID-19 Outbreaks.J Multidiscip Healthc. 2021 Mar 4;14:555-565. doi: 10.2147/JMDH.S302891. eCollection 2021. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2021. PMID: 33707949 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mahase E. Covid-19: WHO declares pandemic because of “alarming levels” of spread, severity, and inaction. BMJ. 2020;368:m1036. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous