Comparative study of four SARS-CoV-2 Nucleic Acid Amplification Test (NAAT) platforms demonstrates that ID NOW performance is impaired substantially by patient and specimen type
- PMID: 32980807
- PMCID: PMC7470790
- DOI: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2020.115200
Comparative study of four SARS-CoV-2 Nucleic Acid Amplification Test (NAAT) platforms demonstrates that ID NOW performance is impaired substantially by patient and specimen type
Abstract
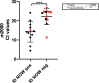
The COVID-19 pandemic in the United States created a unique situation where multiple molecular SARS-CoV-2 diagnostic assays rapidly received Emergency Use Authorization by the FDA and were validated by laboratories and utilized clinically, all within a period of a few weeks. We compared the performance of four of these assays that were evaluated for use at our institution: Abbott RealTime m2000 SARS-CoV-2 Assay, DiaSorin Simplexa COVID-19 Direct, Cepheid Xpert Xpress SARS-CoV-2, and Abbott ID NOW COVID-19. Nasopharyngeal and nasal specimens were collected from 88 ED and hospital-admitted patients and tested by the four methods in parallel to compare performance. ID NOW performance stood out as significantly worse than the other 3 assays despite demonstrating comparable analytic sensitivity. Further study determined that the use of a nasal swab compared to a nylon flocked nasopharyngeal swab, as well as use in a population chronically vs. acutely positive for SARS-CoV-2, were substantial factors.
Keywords: COVID-19; Ct value; Molecular diagnostics; Nasal swab; Nasopharyngeal swab; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Rhoads D.D., Cherian S.S., Roman K., Stempak L.M., Schmotzer C.L., Sadri N. Comparison of Abbott ID Now, Diasorin Simplexa, and CDC FDA EUA methods for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 from nasopharyngeal and nasal swabs from individuals diagnosed with COVID-19. J Clin Microbiol. 2020 doi: 10.1128/jcm.00760-20. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous