Vandetanib for the Management of Advanced Medullary Thyroid Cancer: A Real-World Multicenter Experience
- PMID: 32981301
- PMCID: PMC7520595
- DOI: 10.3803/EnM.2020.687
Vandetanib for the Management of Advanced Medullary Thyroid Cancer: A Real-World Multicenter Experience
Abstract
Background: Vandetanib is the most widely used tyrosine kinase inhibitor for the treatment of patients with advanced medullary thyroid cancer (MTC). However, only limited data regarding its use outside clinical trials are available. We aimed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of vandetanib in patients with advanced MTC in routine clinical practice.
Methods: In this multicenter retrospective study, 12 patients with locally advanced or metastatic MTC treated with vandetanib at four tertiary hospitals were included. The primary outcome was the objective response rate (ORR) based on the Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors. The progression-free survival (PFS), overall survival (OS), and toxicities were also evaluated.
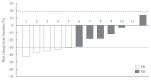
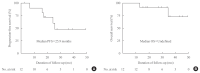
Results: Eleven patients (92%) had distant metastasis and 10 (83%) had disease progression at enrollment. Partial response was observed in five patients (ORR, 42%) and stable disease lasting ≥24 weeks was reported in an additional five patients (83%). During the median 31.7 months of follow-up, disease progression was seen in five patients (42%); of these, two died due to disease progression. The median PFS was 25.9 months, while the median OS was not reached. All patients experienced adverse events (AEs) which were generally consistent with the known safety profile of vandetanib. Vandetanib was discontinued in two patients due to skin toxicity.
Conclusion: Consistent with the phase III trial, this study confirmed the efficacy of vandetanib for advanced MTC in terms of both ORR and PFS in the real-world setting. Vandetanib was well tolerated in the majority of patients, and there were no fatal AEs.
Keywords: Progression-free survival; Protein kinase inhibitors; Thyroid neoplasms; Toxicity.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Real-World Efficacy and Safety of Cabozantinib and Vandetanib in Advanced Medullary Thyroid Cancer.Thyroid. 2021 Mar;31(3):459-469. doi: 10.1089/thy.2020.0206. Epub 2020 Sep 23. Thyroid. 2021. PMID: 32781914
-
Vandetanib for the treatment of advanced medullary thyroid cancer outside a clinical trial: results from a French cohort.Thyroid. 2015 Apr;25(4):386-91. doi: 10.1089/thy.2014.0361. Epub 2015 Feb 18. Thyroid. 2015. PMID: 25627619
-
SAFETY AND TOLERABILITY OF VANDETANIB IN JAPANESE PATIENTS WITH MEDULLARY THYROID CANCER: A PHASE I/II OPEN-LABEL STUDY.Endocr Pract. 2017 Feb;23(2):149-156. doi: 10.4158/EP161259.OR. Epub 2016 Nov 7. Endocr Pract. 2017. PMID: 27819766 Clinical Trial.
-
The safety of vandetanib for the treatment of thyroid cancer.Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2016 Aug;15(8):1107-13. doi: 10.1080/14740338.2016.1201060. Epub 2016 Jul 4. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2016. PMID: 27301016 Review.
-
Cabozantinib and vandetanib for unresectable locally advanced or metastatic medullary thyroid cancer: a systematic review and economic model.Health Technol Assess. 2019 Feb;23(8):1-144. doi: 10.3310/hta23080. Health Technol Assess. 2019. PMID: 30821231 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Neuroendocrine Neoplasms of the Lungs, Thyroid, and Thymus.Biomedicines. 2025 Apr 24;13(5):1028. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13051028. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40426858 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Angiogenic Balance and Its Implications in Cancer and Cardiovascular Diseases: An Overview.Medicina (Kaunas). 2022 Jul 6;58(7):903. doi: 10.3390/medicina58070903. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022. PMID: 35888622 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Real-world clinical profile, RET mutation testing, treatments, and PROs for MTC in Europe.Eur Thyroid J. 2024 Jan 1;13(1):e230172. doi: 10.1530/ETJ-23-0172. Online ahead of print. Eur Thyroid J. 2024. PMID: 38189657 Free PMC article.
-
Sporadic Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma: Towards a Precision Medicine.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Mar 29;13:864253. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.864253. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35422765 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treatment Outcomes and Toxicities of Multiple Tyrosin Kinase Inhibitors for Metastatic Medullary Thyroid Cancer: A Case Series.Biomedicines. 2024 Dec 23;12(12):2923. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12122923. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39767829 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Roman S, Lin R, Sosa JA. Prognosis of medullary thyroid carcinoma: demographic, clinical, and pathologic predictors of survival in 1252 cases. Cancer. 2006;107:2134–42. - PubMed
-
- Droz JP, Rougier P, Goddefroy V, Schlumberger M, Gardet P, Parmentier C. Chemotherapy for medullary cancer of the thyroid. Phase II trials with adriamycin and cis-platinum administered as monochemotherapy. Bull Cancer. 1984;71:195–9. - PubMed
-
- Schwartz DL, Rana V, Shaw S, Yazbeck C, Ang KK, Morrison WH, et al. Postoperative radiotherapy for advanced medullary thyroid cancer: local disease control in the modern era. Head Neck. 2008;30:883–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical