Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2, COVID-19, and the Renin-Angiotensin System: Pressing Needs and Best Research Practices
- PMID: 32981369
- PMCID: PMC7685174
- DOI: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.120.15948
Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2, COVID-19, and the Renin-Angiotensin System: Pressing Needs and Best Research Practices
Abstract
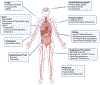
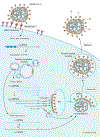
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic is associated with significant morbidity and mortality throughout the world, predominantly due to lung and cardiovascular injury. The virus responsible for COVID-19-severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2-gains entry into host cells via ACE2 (angiotensin-converting enzyme 2). ACE2 is a primary enzyme within the key counter-regulatory pathway of the renin-angiotensin system (RAS), which acts to oppose the actions of Ang (angiotensin) II by generating Ang-(1-7) to reduce inflammation and fibrosis and mitigate end organ damage. As COVID-19 spans multiple organ systems linked to the cardiovascular system, it is imperative to understand clearly how severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 may affect the multifaceted RAS. In addition, recognition of the role of ACE2 and the RAS in COVID-19 has renewed interest in its role in the pathophysiology of cardiovascular disease in general. We provide researchers with a framework of best practices in basic and clinical research to interrogate the RAS using appropriate methodology, especially those who are relatively new to the field. This is crucial, as there are many limitations inherent in investigating the RAS in experimental models and in humans. We discuss sound methodological approaches to quantifying enzyme content and activity (ACE, ACE2), peptides (Ang II, Ang-[1-7]), and receptors (types 1 and 2 Ang II receptors, Mas receptor). Our goal is to ensure appropriate research methodology for investigations of the RAS in patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 and COVID-19 to ensure optimal rigor and reproducibility and appropriate interpretation of results from these investigations.
Keywords: angiotensin II; blood pressure; cardiovascular disease; coronavirus; hypertension.
Figures
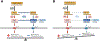
Similar articles
-
Organ-protective effect of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 and its effect on the prognosis of COVID-19.J Med Virol. 2020 Jul;92(7):726-730. doi: 10.1002/jmv.25785. Epub 2020 Apr 5. J Med Virol. 2020. PMID: 32221983 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Is There an Association Between COVID-19 Mortality and the Renin-Angiotensin System? A Call for Epidemiologic Investigations.Clin Infect Dis. 2020 Jul 28;71(15):870-874. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa329. Clin Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32215613 Free PMC article.
-
Disequilibrium between the classic renin-angiotensin system and its opposing arm in SARS-CoV-2-related lung injury.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2020 Aug 1;319(2):L325-L336. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00189.2020. Epub 2020 Jul 8. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32639866 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Two hits to the renin-angiotensin system may play a key role in severe COVID-19.Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2020 Jun;36(6):389-392. doi: 10.1002/kjm2.12237. Epub 2020 Jun 3. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 32492292 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Renin-Angiotensin System: An Important Player in the Pathogenesis of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 28;21(21):8038. doi: 10.3390/ijms21218038. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33126657 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of the renin-angiotensin system in NETosis in the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).Biomed Pharmacother. 2022 Apr;148:112718. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112718. Epub 2022 Feb 14. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022. PMID: 35176710 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of the regulatory mechanism of ACE2 in COVID-19-induced kidney damage with systems genetics approach.J Mol Med (Berl). 2023 Apr;101(4):449-460. doi: 10.1007/s00109-023-02304-9. Epub 2023 Mar 23. J Mol Med (Berl). 2023. PMID: 36951969 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation between kidney sodium and potassium handling and the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in children with hypertensive disorders.Pediatr Nephrol. 2022 Mar;37(3):633-641. doi: 10.1007/s00467-021-05204-7. Epub 2021 Sep 9. Pediatr Nephrol. 2022. PMID: 34499251 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19-Associated Cerebrovascular Events: A Case Series Study and a Literature Review of Possible Mechanisms.Case Rep Neurol. 2023 Feb 3;15(1):11-23. doi: 10.1159/000529122. eCollection 2023 Jan-Dec. Case Rep Neurol. 2023. PMID: 36748059 Free PMC article.
-
Association of adiposity and its changes over time with COVID-19 risk in older adults with overweight/obesity and metabolic syndrome: a longitudinal evaluation in the PREDIMED-Plus cohort.BMC Med. 2023 Oct 13;21(1):390. doi: 10.1186/s12916-023-03079-z. BMC Med. 2023. PMID: 37833678 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Hoffmann M, Kleine-Weber H, Schroeder S, Kruger N, Herrler T, Erichsen S, Schiergens TS, Herrler G, Wu NH, Nitsche A, Muller MA, Drosten C, Pohlmann S. Sars-cov-2 cell entry depends on ace2 and tmprss2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor. Cell. 2020;181:271–280 e278 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tipnis SR, Hooper NM, Hyde R, Karran E, Christie G, Turner AJ. A human homolog of angiotensin-converting enzyme. Cloning and functional expression as a captopril-insensitive carboxypeptidase. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:33238–33243 - PubMed
-
- Donoghue M, Hsieh F, Baronas E, Godbout K, Gosselin M, Stagliano N, Donovan M, Woolf B, Robison K, Jeyaseelan R, Breitbart RE, Acton S. A novel angiotensin-converting enzyme-related carboxypeptidase (ace2) converts angiotensin i to angiotensin 1–9. Circ Res. 2000;87:E1–9 - PubMed
-
- Masi S, Uliana M, Virdis A. Angiotensin ii and vascular damage in hypertension: Role of oxidative stress and sympathetic activation. Vascul Pharmacol. 2019;115:13–17 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL128355/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX000893/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- P01 HL095070/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K23 HL148394/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI120698/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL136348/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK118019/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI120698/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI110173/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK104785/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL146818/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- L40 HL148910/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

