Performance of Glow Fixation GoCheck Kids and 2WIN Photoscreeners and Retinomax to Uncover Hyperopia
- PMID: 32982148
- PMCID: PMC7500080
- DOI: 10.2147/OPTH.S256991
Performance of Glow Fixation GoCheck Kids and 2WIN Photoscreeners and Retinomax to Uncover Hyperopia
Abstract
Background: A low-detail, glowing fixation device was added to GoCheck Kids (GCK) photoscreener in the hope of unmasking hyperopia and amblyopia risk factors (ARF).
Methods: Pediatric eye patients were screened by GCK and 2WIN photoscreeners, and Retinomax autorefractor before being compared to AAPOS ARFs.
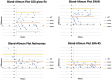
Results: Screening was attempted by 131 children who then had school bus accommodation-relaxing skiascopy (SBA-RS) before cycloplegic examination. By 2013 AAPOS uniform guidelines, sensitivity/specificity for GCK was 87%/68%, for 2WIN 87%/71% and for Retinomax 79%/68%. Detection of amblyopia had sensitivity/specificity by GCK of 78%/63%, for 2WIN 79%/65% and for Retinomax 77%/68%. Inconclusive screens were seven for GCK, six for 2WIN and 13 for Retinomax. Mean hyperopia for GCK (+2.49±0.74 D) was similar to cycloplegic refraction (+2.93±0.72 D) and SBA-RS (+2.80±0.82 D) while GCK was slightly more than Retinomax (+1.59±0.93 D, p=0.13) but significantly more than 2WIN (+1.02±0.49 D, p<0.01).
Conclusion: GCK, 2WIN and Retinomax had similar validity detecting uniform amblyopia risk factors and amblyopia itself. The nondetailed glow fixation device allowed GCK to uncover substantial hyperopia while the detailed flashing fixation devices on 2WIN and Retinomax seemed to stimulate accommodation in some hyperopic children.
Clinical trials registry: NCT04297969. Data Access: http://www.abcd-vision.org/references/GCK%20glow%202WIN%20deidentify.pdf.
Précis: A glow fixation device on a smart phone photoscreener allowed robust detection of hyperopia.
Keywords: amblyopia risk factor; hyperopia; photoscreener; vision screening.
© 2020 Levitt et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Miss Alexa Levitt reports grants from Ingram Scholars Program, during the conduct of the study; in addition, Miss Alexa Levitt has a patent glowing fixation device pending; and at the time this study was conducted she was an intern at GoCheck and finishing her undergraduate degree at Vanderbilt University. The Ingram Scholars Program (undergraduate merit scholarship program) awarded her the necessary funding to support her travel expenses from Nashville, TN (where the GoCheck office is) to Anchorage, AK (where Alaska Blind Child Discovery is). She worked with Dr Robert Arnold in his clinic on behalf of the Clinical team at GoCheck. Dr Arnold is a board member of Glacier Medical Software and PDI Check. He coordinates the Alaska Blind Child Discovery project and is an unpaid member of an advisory board to several photoscreeners including GoCheck Kids and Adaptica. Dr Arnold is an investigator and protocol developer with the NIH-supported Pediatric Eye Disease Investigator Group. Dr Arnold is a nonpaid advisory board member for PlusoptiX and iScreen, during the conduct of the study. He coordinates remote medical mission outreach that has received donations from several vendors for Burma Vision, outside the submitted work. In addition, Dr Robert W Arnold has a patent PDI Check pending to Robert W. Arnold and Alex Damarjian. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

