Immunoregulatory Roles of Extracellular Vesicles and Associated Therapeutic Applications in Lung Cancer
- PMID: 32983146
- PMCID: PMC7483575
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.02024
Immunoregulatory Roles of Extracellular Vesicles and Associated Therapeutic Applications in Lung Cancer
Abstract
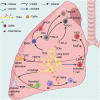
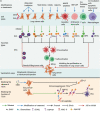
Lung cancer represents a fatal condition that has the highest morbidity and mortality among malignancies. The currently available treatments fall short of improving the survival and quality of life of late-stage lung cancer patients. Extracellular vesicles (EVs) secreted by tumors or immune cells transport proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids to other cells, thereby mediating immune regulation in the tumor microenvironment. The cargo carried by EVs vary by cellular state or extracellular milieu. So far, multiple studies have suggested that EVs from lung tumor cells (TEVs) or immune cells promote tumor progression mainly through suppressing antitumor immunity. However, modified or engineered EVs can be used as vaccines to elicit antitumor immunity. In addition, blocking the function of immunosuppressive EVs and using EVs carrying immunogenic medicine or EVs from certain immune cells also shows great potential in lung cancer treatment. To provide information for future studies on the role of EVs in lung cancer immunity, this review focus on the immunoregulatory role of EVs and associated treatment applications in lung cancer.
Keywords: extracellular vesicles; immunostimulation; immunosuppression; lung cancer; therapeutic application.
Copyright © 2020 Yin, Fan, Xu, Wu, Li, Zhou, Liao, Duan, Wang, Geng and Jin.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Tumor-derived extracellular vesicles: Regulators of tumor microenvironment and the enlightenment in tumor therapy.Pharmacol Res. 2020 Sep;159:105041. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105041. Epub 2020 Jun 21. Pharmacol Res. 2020. PMID: 32580030 Review.
-
Extracellular Vesicles: New Endogenous Shuttles for miRNAs in Cancer Diagnosis and Therapy?Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 4;21(18):6486. doi: 10.3390/ijms21186486. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32899898 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Focus on Extracellular Vesicles: New Frontiers of Cell-to-Cell Communication in Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Feb 6;17(2):175. doi: 10.3390/ijms17020175. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 26861306 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Apoptotic Tumor Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles as Important Regulators of the Onco-Regenerative Niche.Front Immunol. 2018 May 23;9:1111. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01111. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29875772 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Use of Tumor Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1660:433-440. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7253-1_35. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28828677
Cited by
-
Development of Extracellular Vesicle Therapeutics: Challenges, Considerations, and Opportunities.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Sep 20;9:734720. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.734720. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34616741 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A systematic review of extracellular vesicles as non-invasive biomarkers in glioma diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment response monitoring.Mol Biol Rep. 2021 Oct;48(10):6971-6985. doi: 10.1007/s11033-021-06687-1. Epub 2021 Aug 30. Mol Biol Rep. 2021. PMID: 34460059
-
Strategies for Small Extracellular Vesicle-Based Cancer Immunotherapy.Research (Wash D C). 2024 Jul 22;7:0421. doi: 10.34133/research.0421. eCollection 2024. Research (Wash D C). 2024. PMID: 39040921 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Extracellular Vesicles from Human Macrophages on Host-Pathogen Interaction.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 23;22(19):10262. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910262. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34638604 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Apoptotic tumor cell-derived microparticles loading Napabucasin inhibit CSCs and synergistic immune therapy.J Nanobiotechnology. 2023 Feb 2;21(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s12951-023-01792-8. J Nanobiotechnology. 2023. PMID: 36732759 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fred RH, Scagliotti GV, Mulshine JL, Kwon R, Curran WJ, Jr., Wu Y-L, et al. Lung cancer: current therapies and new targeted treatments. Lancet. (2017) 389:299–311. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

