ICOS+ Tregs: A Functional Subset of Tregs in Immune Diseases
- PMID: 32983168
- PMCID: PMC7485335
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.02104
ICOS+ Tregs: A Functional Subset of Tregs in Immune Diseases
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: ICOS+ Tregs: A Functional Subset of Tregs in Immune Diseases.Front Immunol. 2021 May 12;12:701515. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.701515. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34054885 Free PMC article.
Abstract
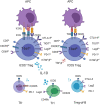
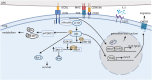
Recent studies have reported the pathological effect of ICOS+ T cells, but ICOS signals also widely participate in anti-inflammatory responses, particularly ICOS+ regulatory T (Treg) cells. The ICOS signaling pathway endows Tregs with increased generation, proliferation, and survival abilities. Furthermore, there is enough evidence to suggest a superior capacity of ICOS+ Tregs, which is partly attributable to IL-10 induced by ICOS, yet the associated mechanism needs further investigation. In this review, we discuss the complicated role of ICOS+ Tregs in several classical autoimmune diseases, allergic diseases, and cancers and investigate the related therapeutic applications in these diseases. Moreover, we identify ICOS as a potential biomarker for disease treatment and prognostic prediction. In addition, we believe that anti-ICOS/ICOSL monoclonal antibodies exhibit excellent clinical application potential. A thorough understanding of the effect of ICOS+ Tregs and the holistic role of ICOS toward the immune system will help to improve the therapeutic schedule of diseases.
Keywords: ICOS; Treg cells; autoimmune disease; immunotherapy; neoplasm.
Copyright © 2020 Li and Xiong.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

