Cytokine Storm in COVID-19: "When You Come Out of the Storm, You Won't Be the Same Person Who Walked in"
- PMID: 32983172
- PMCID: PMC7492381
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.02132
Cytokine Storm in COVID-19: "When You Come Out of the Storm, You Won't Be the Same Person Who Walked in"
Abstract
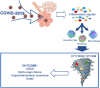
In December 2019, a novel coronavirus, COVID-19, was discovered to be the causal agent of a severe respiratory infection named SARS-CoV-2, and it has since been recognized worldwide as a pandemic. There are still numerous doubts concerning its pathogenesis and particularly the underlying causes of the various clinical courses, ranging from severe manifestations to asymptomatic forms, including acute respiratory distress syndrome. The major factor responsible for acute respiratory distress syndrome is the so-called "cytokine storm," which is an aberrant response from the host immune system that induces an exaggerated release of proinflammatory cytokines/chemokines. In this review, we will discuss the role of cytokine storm in COVID-19 and potential treatments with which counteract this aberrant response, which may be valuable in the clinical translation.
Keywords: SARS-CoV2; acute respiratory distress; coronavirus; cytokines; inflammation; severity.
Copyright © 2020 Castelli, Cimini and Ferri.
Figures
References
-
- WHO WHO Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Dashboard. Available online at: https://covid19.who.int/ (accessed July 31, 2020).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous