Knockdown of LINC00665 inhibits proliferation and invasion of breast cancer via competitive binding of miR-3619-5p and inhibition of catenin beta 1
- PMID: 32983239
- PMCID: PMC7513511
- DOI: 10.1186/s11658-020-00235-8
Knockdown of LINC00665 inhibits proliferation and invasion of breast cancer via competitive binding of miR-3619-5p and inhibition of catenin beta 1
Abstract
Background: Long intergenic non-protein coding RNA00665 (LINC00665) plays a crucial tumorigenic role in many cancers, such as gastric cancer and lung adenocarcinoma. However, its role and mechanism of action in the progression of breast cancer (BC) are unknown.
Methods: LINC00665 expression levels were determined using quantitative polymerase chain reaction analysis with BC tissues and cell lines. BC cell proliferation was tested by performing 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide assays, whereas BC cell migration and invasion capabilities were analyzed by performing transwell migration assays. Percentages of apoptotic cells were measured by flow cytometry. Interactions between LINC00665 and miR-3169-5p were examined by performing luciferase reporter assays, and the expression levels of proteins, such as β-catenin, were examined by western blot analysis.
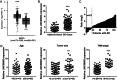
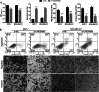
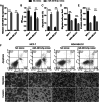
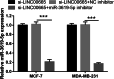
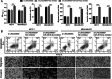
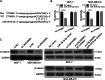
Results: LINC00665 was expressed at high levels in BC tissues and cells. Upregulated LINC00665 expression correlated with tumor size and tumor, node, and metastasis stages, but not with the age of patients. LINC00665 knockdown inhibited BC cell proliferation, migration, and invasion, whereas it promoted apoptosis. Moreover, bioinformatics analysis and the luciferase reporter assay revealed that LINC00665 bound the microRNA (miR) miR-3619-5p. miR-3619-5p expression correlated negatively with LINC00665 expression in BC tissues. miR-3619-5p overexpression inhibited BC cell proliferation, migration, and invasion, but promoted apoptosis. Simultaneous knockdown of LINC00665 and miR-3619-5p led to increased cell proliferation, migration, and invasion, and inhibited apoptosis. Additionally, catenin beta 1, which encodes the β-catenin protein, was the target gene of miR-3619-5p. β-catenin expression clearly decreased after LINC00665 knockdown and miR-3619-5p overexpression, but increased after simultaneous knockdown of LINC00665 and miR-3619-5p.
Conclusion: LINC00665 knockdown inhibited BC cell proliferation and invasion by binding miR-3619-5p and inhibiting β-catenin expression.
Keywords: Breast cancer; CTNNB1; LINC00665; miR-3619-5p; β-Catenin.
© The Author(s) 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
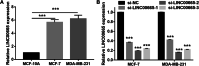

References
-
- Walsh T, Casadei S, Coats KH, Swisher E, Stray SM, Higgins J, Roach KC, Mandell J, Lee MK, Ciernikova S, Foretova L, Soucek P, King MC. Spectrum of mutations in BRCA1, BRCA2, CHEK2, and TP53 in families at high risk of breast cancer. JAMA. 2006;295:1379–1388. - PubMed
-
- Shen XH, Qi P, Du X. Long non-coding RNAs in cancer invasion and metastasis. Mod Pathol. 2015;28:4–13. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

