Bronchopleural fistula development in the setting of novel therapies for acute respiratory distress syndrome in SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia
- PMID: 32983308
- PMCID: PMC7500914
- DOI: 10.1016/j.radcr.2020.09.026
Bronchopleural fistula development in the setting of novel therapies for acute respiratory distress syndrome in SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia
Abstract
COVID-19 pneumonia has demonstrated a wide spectrum of clinical presentations that has yet to be completely uncovered. We discuss the case of a 49-year-old male who presented to the emergency department with fever, cough, and shortness of breath. Initial chest X-ray suggested viral pneumonia that was confirmed to be due to COVID-19. He was treated with empiric antibiotics, antiviral therapy, high-dose glucocorticoids, and interleukin antagonists. Two weeks into the patient's hospital course, he rapidly decompensated with subsequent chest X-ray and CT chest confirming tension pneumothorax with bronchopleural fistula. Intraoperative samples of the necrotic empyema identified mucormycosis invading the lung parenchyma with follow-up microbiology results confirming Rhizopus species. In this case report, we explore the possibility that the patient's immunocompromised state may have contributed to the patient's development of mucormycosis and subsequent development of bronchopleural fistula.
Keywords: COVID; Dexamethasone; Mucormycosis; Pneumonia; Remdesivir; Tocilizumab.
Published by Elsevier Inc. on behalf of University of Washington.
Figures

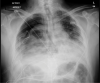
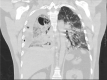

References
-
- Cai Y, Hao Z, Gao Y, Ping W, Wang Q, Peng S. Coronavirus disease 2019 in the perioperative period of lung resection: a brief report from a single thoracic surgery Department in Wuhan, People’s Republic of China. J Thorac Oncol. 2020;15(6):1065–1072. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2020.04.003. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

