Effects of different ablation points of renal denervation on the efficacy of resistant hypertension
- PMID: 32983640
- PMCID: PMC7500320
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.9842
Effects of different ablation points of renal denervation on the efficacy of resistant hypertension
Abstract
Objective: To explore the blood pressure response to different ablation points of renal denervation (RDN) in patients with resistant hypertension.
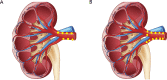
Methods: A total of 42 cases with resistant hypertension treated by RDN in our center from 2013 to 2015 were retrospectively analyzed. The patients were divided into two groups according to the different ablation points of RDN: the standard treatment group (spiral ablation from near to proximal, with less than 8 points per artery) and the intensive treatment group (from near to far by spiral ablation, with at least 8 points per artery), with 21 patients in each group. The ablation parameters, including points, impedance, actual wattage, and actual temperature, were recorded intraoperatively. Renal angiography was performed again after RDN. Ambulatory blood pressure (ABP) images were taken for all patients at the baseline and 6 months after operation.
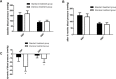
Results: The mean 24-h blood pressure of the standard treatment group was lower than that of the baseline (24-h systolic blood pressure decreased by 7.4 ± 10.6 mmHg and 24-h diastolic blood pressure decreased by 4.6 ± 6.1 mmHg), and the mean 24-h blood pressure decreased significantly from baseline to 6 months in the intensive treatment group (24-h systolic blood pressure decreased by 27.4 ± 11.4 mmHg, P < 0.0001; 24-h diastolic blood pressure decreased by 10.9 ± 9.6 mmHg, P = 0.005). There was a positive correlation between the decrease of systolic/diastolic 24-hour mean and the number of ablation points used in the procedure. The mean value of systolic and diastolic blood pressure was positively correlated with ablation points at 24-hour (R 2 = 0.777 and 0.633 respectively, P < 0.01). There were no adverse events in either group after the operation and during the follow-up.
Conclusions: RDN could significantly reduce BP in patients with resistant hypertension. Our study showed that the antihypertensive effect appeared to be positively correlated with the number of ablation points.
Keywords: Ablation points; Resistant hypertension.
©2020 Zhang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Blood pressure response to catheter-based renal sympathetic denervation in severe resistant hypertension: data from the Greek Renal Denervation Registry.Clin Res Cardiol. 2017 May;106(5):322-330. doi: 10.1007/s00392-016-1056-z. Epub 2016 Dec 12. Clin Res Cardiol. 2017. PMID: 27957627
-
Renal denervation in moderate treatment-resistant hypertension.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013 Nov 12;62(20):1880-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2013.06.023. Epub 2013 Jul 10. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 23850901 Clinical Trial.
-
Renal nerve stimulation: complete versus incomplete renal sympathetic denervation.Blood Press. 2021 Dec;30(6):376-385. doi: 10.1080/08037051.2021.1982376. Epub 2021 Oct 14. Blood Press. 2021. PMID: 34647513
-
2019 Consensus Statement of the Taiwan Hypertension Society and the Taiwan Society of Cardiology on Renal Denervation for the Management of Arterial Hypertension.Acta Cardiol Sin. 2019 May;35(3):199-230. doi: 10.6515/ACS.201905_35(3).20190415A. Acta Cardiol Sin. 2019. PMID: 31249454 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Renal Denervation for Resistant Hypertension in the contemporary era: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Sci Rep. 2019 Apr 17;9(1):6200. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-42695-9. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30996305 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Azizi M, Sapoval M, Gosse P, Monge M, Bobrie G, Delsart P, Midulla M, Mounier-Véhier C, Cour PY, Lantelme P, Denolle T, Dourmap-Collas C, Trillaud H, Pereira H, Plouin PF, Chatellier G, Renal Denervation for Hypertension (DENERHTN) investigators Optimum and stepped care standardized antihypertensive treatment with or without renal denervation for resistant hypertension (DENERHTN): a ulticentre, openlabel, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2015;385(9981):1957–1965. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61942-5. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bertog S, Fischel TA, Vega F, Ghazarossian V, Pathak A, Vaskelyte L, Kent D, Sievert H, Ladich E, Yahagi K, Virmani R. Randomised, blinded and controlled comparative study of chemical and radiofrequency-based renal denervation in a porcine model. EuroIntervention. 2017;12(15):e1898–e1906. doi: 10.4244/EIJ-D-16-00206. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bhatt DL, Kandzari DE, O’Neill WW. A controlled trial of renal denervation for resistant hypertension. Journal of Vascular Surgery. 2014;370:1393–1401. - PubMed
-
- Calhoun DA, Jones D, Textor S, Goff DC, Murphy TP, Toto RD, White A, Cushman WC, White W, Sica D, Ferdinand K, Giles TD, Falkner B, Carey RM. Resistant hypertension: diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment. A scientific statement from the American Heart Association Professional Education Committee of the Council for High Blood Pressure Research. Hypertension. 2008;51(6):1403–1419. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.108.189141. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

