Mycobacterium abscessus Infection after Breast Lipotransfer: A Report of 2 Cases
- PMID: 32983807
- PMCID: PMC7489723
- DOI: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000003063
Mycobacterium abscessus Infection after Breast Lipotransfer: A Report of 2 Cases
Abstract
Mycobacterium abscessus is a rare, non-tuberculous, rapidly growing mycobacterium. Although it has been usually associated with chronic pulmonary infections in cystic fibrosis patients, the second most frequent infection sites are the skin and subcutaneous tissue. Most of the cutaneous infections described in the literature occur secondary to cosmetic invasive procedures, many of them in the context of medical tourism. Its atypical presentation and antibiotic-resistant nature make its diagnosis and therapeutics challenging. In this case report, we present 2 cases of M. abscessus infections secondary to breast lipotransfer reported in the same private center. Case 1 patient underwent surgery to treat scar contracture resulting from previous quadrantectomy. Case 2 patient underwent breast augmentation with lipotransfer. Both of them developed lesions in the breast and in the donor site (abdomen). The therapeutic regimen used was amikacin (1 g/24 h) + tigecycline (50 mg/12 h). In case 1, we performed a simple mastectomy, and in case 2, periodical ultrasound-guided drainages were performed as additional procedures. To our knowledge, these are the first 2 cases that describe an infection secondary to breast lipotransfer. The aim of our report was to illustrate the presentation, diagnosis, therapeutic management, and strategies available to prevent this complication.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of The American Society of Plastic Surgeons.
Figures

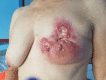
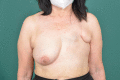
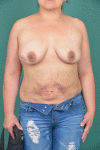
References
-
- Fox LP, Geyer AS, Husain S, et al. Mycobacterium abscessus cellulitis and multifocal abscesses of the breasts in a transsexual from illicit intramammary injections of silicone. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50:450. - PubMed
-
- Medjahed H, Gaillard JL, Reyrat JM. Mycobacterium abscessus: a new player in the mycobacterial field. Trends Microbiol. 2010;18:117–123 - PubMed
-
- Agarwal A, Maloney RW. Mycobacterium abscessus outbreak after rhytidectomies performed in an outpatient surgery center. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2011;128:85e–86e - PubMed
-
- Wu CH, Thong HY, Huang CC, et al. Report of two cases of cutaneous Mycobacterium abscessus infection complicating professional decorative tattoo. Dermatol Sin. 2017;35:40–43
-
- Cusumano LR, Tran V, Tlamsa A, et al. Rapidly growing Mycobacterium infections after cosmetic surgery in medical tourists: the Bronx experience and a review of the literature. Int J Infect Dis. 2017;63:1–6 - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
